Published by: Zaya
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
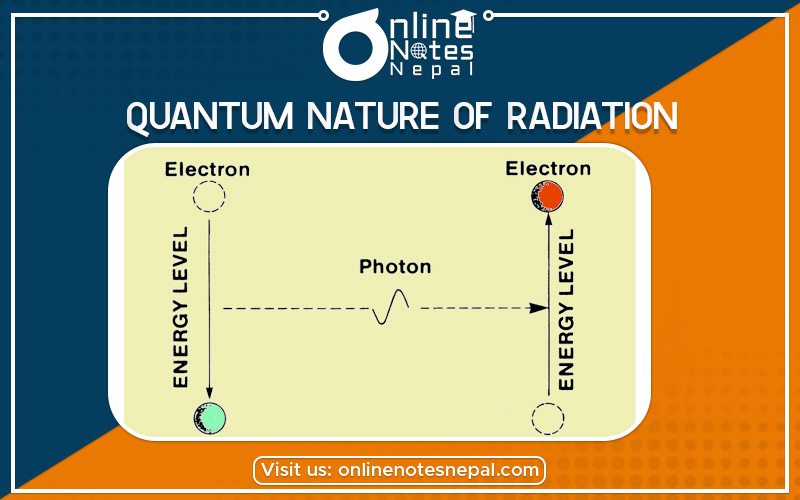
According to Einstein’s photoelectric equation, the total amount of incident energy on the metal surface is used for the work function of the metal surface and kinetic energy of the emitted electron.
According to Einstein, the light of frequency ‘f’ consist of photons each of energy ‘hf’ fall on the metal surface, the energy is completely transferred to a free electron in the metal. Then the electrons are emitted with velocity ‘V’.
According to Einstein photoelectric equation Energy of photon=Work function + K.E of electron
or, E=0+K.E
or,hf=hf0+1/2mv^2 max
Where h is planks constant whose value is 6.626*10-34
f=frequency of energy
fo=threshold frequency
0=work function
m=mass of electrons
or,hf=hf0+evo

where
ʎ=wavelength.
ʎ0=threshold wavelength.

(I)The photoelectric effect is possible only when the frequency of incident light is greater than the threshold frequency.
(II)The number of photoelectrons emitted depends on the intensity of light-exposed but independent of the frequency of incident
light.
(III)The velocity of photoelectrons emitted is independent of the intensity of incident light but depends on the frequency of incident light.
(IV)The photoelectric emission of electrons without any significant delay as soon as the light of suitable energy incident.