Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 30 Jan 2022

Bee is the main source of honey. Honey is a very nutritious food. Bee is called a social insect. It lives in the group and performs collective works. Bee collects nectar from different types of flowers to prepare honey.

Bees find their food by their own from nature. So in the case of bees, the ones who are farming should not worry about food and their balanced diet.
Natural Sources of Food: The natural sources of food for bees are the flowers, plants, fruits orchards, different agricultural crops and pasture land which are developed for bees. Bees require nectar and pollen for preparing their food which they collect from various types of flowers or herbs. They get propolis from plant sources.

Bees need artificial feeding only in some cases, for the following reasons:
Beekeepers give fine sugar syrup or honey for the colony. In the winter season, thebees need an artificial source like sugar syrup because only natural sources aren't enough. The syrup may have a concentration from 30% to 60% depending on the purpose and season of feeding. For example, autumn feeding is done in high concentration to meet winter scarcities and spring feeding is done in low concentration to induce the queen for reproduction. Bees can be fed internally or externally. To feed externally, a clean piece of cotton cloth soaked in sugar syrup is put in a tray and placed 2 to 3 meters away from the entrance of the hive. Similarly, to feed internally within the hive, special feeders in several ways can be purchased from the market. They are generally placed in brooding chamber to serve sugar syrup.
There are some of the essential materials for bees for their survival which are collected from plant sources. Bees collect these materials from pasture. They are as follows:
Nectar: Nectar contains dextrose, sucrose, and cellulose. Bees suck nectar from flowers. Nectar contains 80% of water. Bees process the nectar in the hive and reduces water level to 20% when the honey is ready to harvest.
Pollen: Pollen is very important for the worker bees. They collect it in pollen basket located beside hind legs. They consume pollen for their own growth. A bee can collect about 0.1 gram of pollen on a normal day.
Propolis: Propolis is also an important material for a beehive and gives support to comb. They find it from the secretions or sap of plants and carry on their pollen basket.
Water: Bees cannot eat honey in semi-solid form. During winter, they eat honey by adding water. During summer, they collect water to keep their environment cold.

Bee Wax: Bees prepare wax through their wax glands. Bees consume a lot of honey to prepare a little wax. They prepare combs and cells using wax.
Bees can manage their food by own from the natural sources. They travel a long distance in search of their food. Therefore, we must manage pasture land for them. It is also important to consider the appropriate selection of plants for them. The different floral sources for the bee can be grown, for instance, in the pasture land. Bee’s hive can also be moved to a distant place in a season where the sources are available.
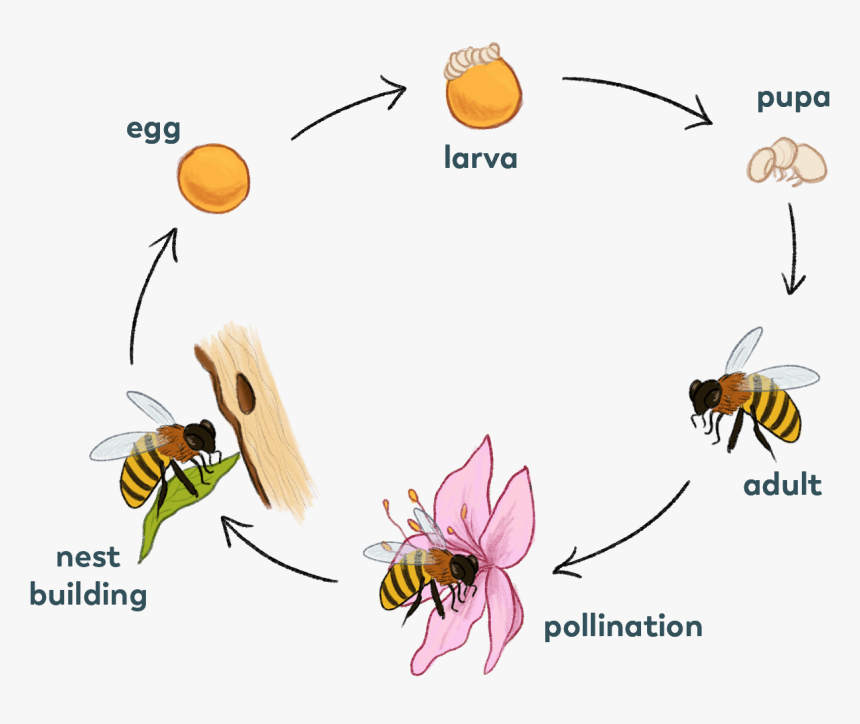
The life cycle of bees passes through four broad and distinct stages such as egg, larva, pupa and adult. Their time frame is represented in the following table:
|
Type |
Egg |
Larva |
Pupa |
Total days |
Adult’s lifetime |
|
Queen |
3 days |
5 days |
7-8 days |
15-16 days |
3-4 years |
|
Drone |
3 days |
7 days |
14 days |
24 days |
Maximum 57 days |
|
Worker |
3 days |
6 days |
11-12 days |
20-21 days |
5-6 month (6 weeks during peak time) |
The queen is a female and single in a colony and an organizer of the colony. She mates with drones for her life and lays fertile or unfertile eggs. Drones die after mating. Drones are developed from unfertile eggs. All workers are female and virgin for the whole life.
The main purpose of bee farming is maximizing profit from selling honey. There are several aspects of production management. It is important to firstly clarify the objective of management. The other aspects are harvesting techniques, processing techniques, packing, selling and branding methods, marketing modality, storage techniques and so on. And, mainly managing the records is avery important aspect of production management.
Prevention and Control of Diseases, Predators, and Parasites
Predators: Wasps, Moths, Ants, Mites
Diseases: Dysentery, Paralysis, Foul board
In order to secure bees from the diseases and predators, it is advisable to consult with the reliable technologists.