Published by: Dikshya
Published date: 25 Jun 2023
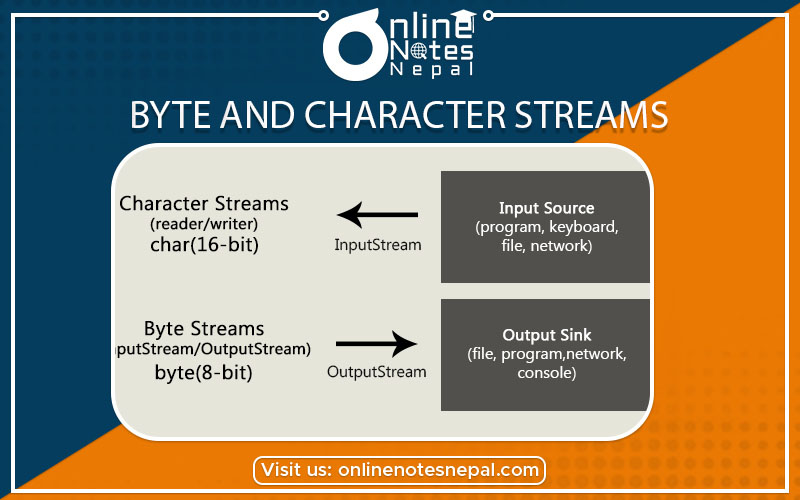
Byte streams
Byte streams, also known as binary streams, are used for reading and writing binary data at the byte level. They deal with data as a sequence of individual bytes, without any interpretation or manipulation of the data. Byte streams are particularly useful for handling non-textual data, such as images, audio, video, or any other kind of binary files.
In most programming languages, byte streams consist of two fundamental operations:
Input: Byte streams allow you to read data from a source, such as a file or a network socket, into your program. You can read data in fixed-sized chunks or even one byte at a time, depending on your requirements. Byte streams provide methods to read bytes and byte arrays.
Output: Byte streams enable you to write data from your program to a destination, such as a file or a network socket. You can write data in fixed-sized chunks or one byte at a time. Byte streams provide methods to write bytes and byte arrays.
Byte streams are commonly used for tasks such as:
In Java, some commonly used byte stream classes include InputStream and its subclasses (FileInputStream, ByteArrayInputStream, etc.) for input operations, and OutputStream and its subclasses (FileOutputStream, ByteArrayOutputStream, etc.) for output operations.
Character Streams:
Character streams, also known as text streams, are used for reading and writing text-based data at the character level. They provide a higher-level abstraction over byte streams by handling character encoding and decoding, allowing you to work with text in a more convenient and portable manner.
Character streams are particularly useful when dealing with text files, processing user input, or transmitting text-based data. They handle the conversion between the platform's default character encoding and the specified character encoding, ensuring that characters are correctly represented.
Character streams offer two fundamental operations:
Input: Character streams allow you to read text data from a source, such as a file or a network socket, into your program. You can read data as characters, lines, or even entire files. Character streams provide methods to read characters, strings, or lines of text.
Output: Character streams enable you to write text data from your program to a destination, such as a file or a network socket. You can write characters, strings, or lines of text. Character streams provide methods to write characters or strings.
Character streams are commonly used for tasks such as:
In Java, some commonly used character stream classes include Reader and its subclasses (FileReader, InputStreamReader, etc.) for input operations, and Writer and its subclasses (FileWriter, OutputStreamWriter, etc.) for output operations.