Published by: Zaya
Published date: 18 Jun 2021

Operating systems are there from the very first computer generation and they keep evolving with time. Some of the important types of operating systems that are most commonly used are:
This type of operating system does not interact with the computer directly. There is an operator which takes similar jobs having the same requirement and groups them into batches. It is the responsibility of the operator to sort the jobs with similar needs.
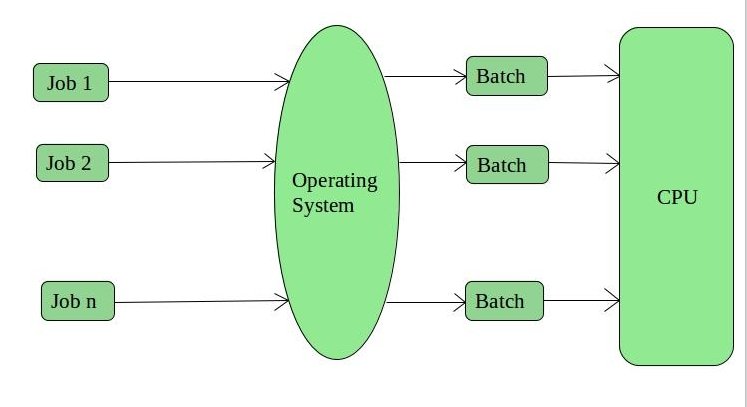
fig. Batch Operating System[/caption]
Advantages of Batch Operating System:
Disadvantages of Batch Operating System:
Each task has given some time to execute so that all the tasks work smoothly. Each user gets the time of CPU as they use a single system. These systems are also known as Multitasking Systems. The task can be from a single user or from different users also. The time that each task gets to execute is called quantum. After this time interval is over OS switches over to the next task.
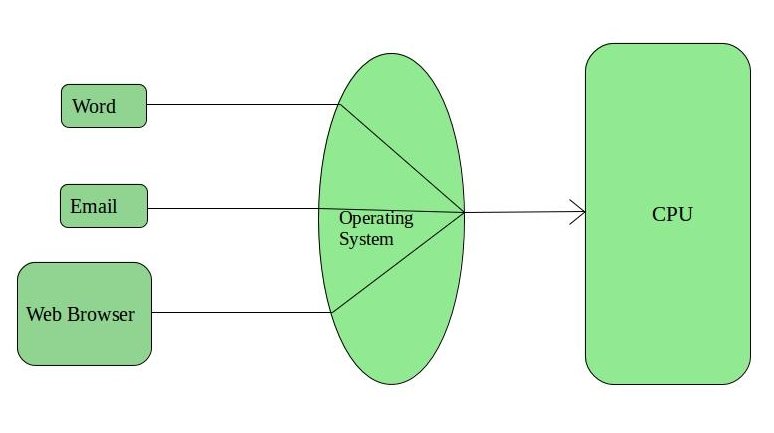
Advantages of Time-Sharing OS:
Disadvantages of Time-Sharing OS:
These types of the operating system is a recent advancement in the world of computer technology and are being widely accepted all over the world and, that too, with a great pace. Various autonomous interconnected computers communicate with each other using a shared communication network. Independent systems possess their own memory unit and CPU. These are referred to as loosely coupled systems or distributed systems. These system's processors differ in size and function. The major benefit of working with these types of the operating system is that it is always possible that one user can access the files or software which are not actually present on his system but on some
other system connected within this network i.e., remote access is enabled within the devices connected in that network.
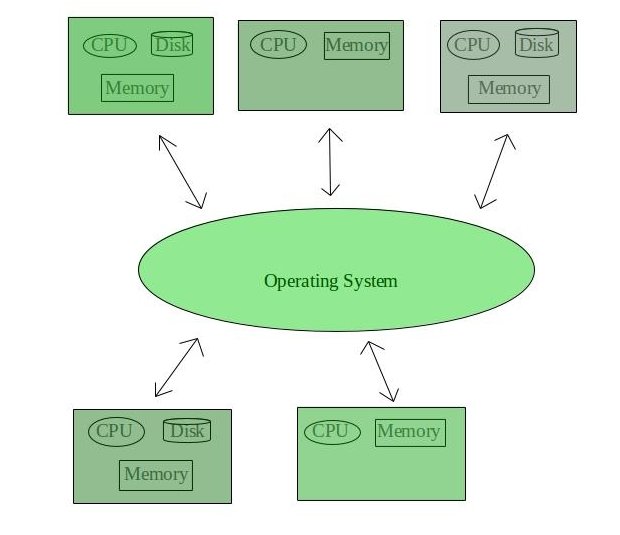
Advantages of Distributed Operating System:
Disadvantages of Distributed Operating System:
These systems run on a server and provide the capability to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. These type of operating systems allows shared access of files, printers, security, applications, and other networking functions over a small private network. One more important aspect of Network Operating Systems is that all the users are well aware of the underlying configuration, of all other users within the network, their individual connections, etc. and that’s why these computers are popularly known as tightly coupled systems.
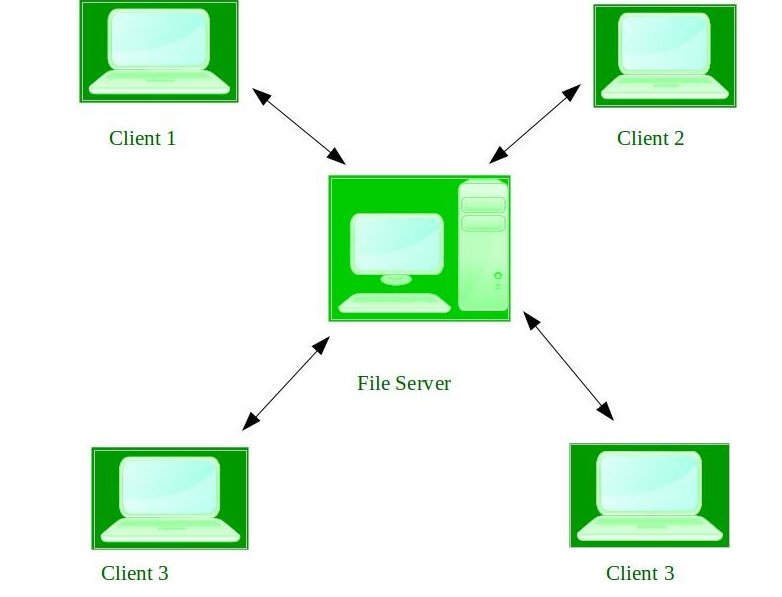
fig. Network Operating System[/caption]
Advantages of Network Operating System:
Disadvantages of Network Operating System:
A real-time system is defined as a data processing system in which the time interval required to process and respond to inputs is so small that it controls the environment. The time taken by the system to respond to an input and display of required updated information is termed the response time. So in this method, the response time is very less as compared to online processing. Real-time systems are used when there are rigid time requirements on the operation of a processor or the flow of data and real-time systems can be used as a control device in a dedicated application.
A real-time operating system must have well-defined, fixed time constraints, otherwise, the system
will fail. For example, Scientific experiments, medical imaging systems, industrial control systems, weapon systems, robots, air traffic control systems, etc.
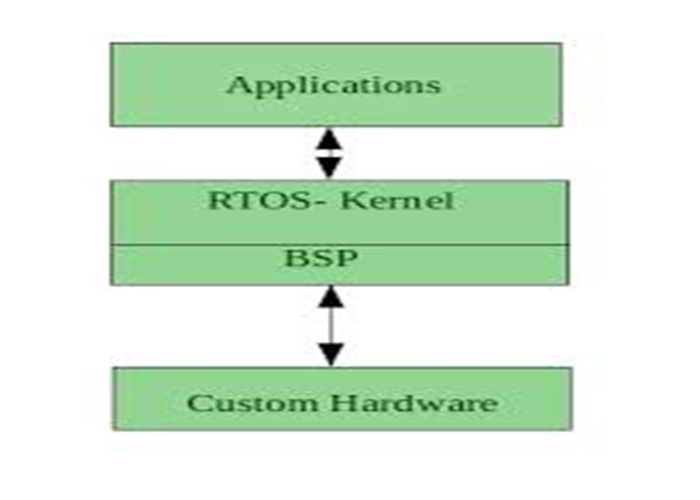
Advantages of Real-Time Operating System:
Disadvantages of Real-Time Operating System:
I. Hard real-time systems
Hard real-time systems guarantee that critical tasks complete on time. In hard real-time systems, secondary storage is limited or missing and the data is stored in ROM. In these systems, virtual memory is almost never found.
II. Soft real-time systems
Soft real-time systems are less restrictive. A critical real-time task gets priority over other tasks and retains the priority until it completes. Soft real-time systems have limited utility than hard real-time systems. For example, multimedia, virtual reality, Advanced Scientific Projects like undersea exploration and planetary rovers, etc.