Published by: Zaya
Published date: 22 Jun 2021

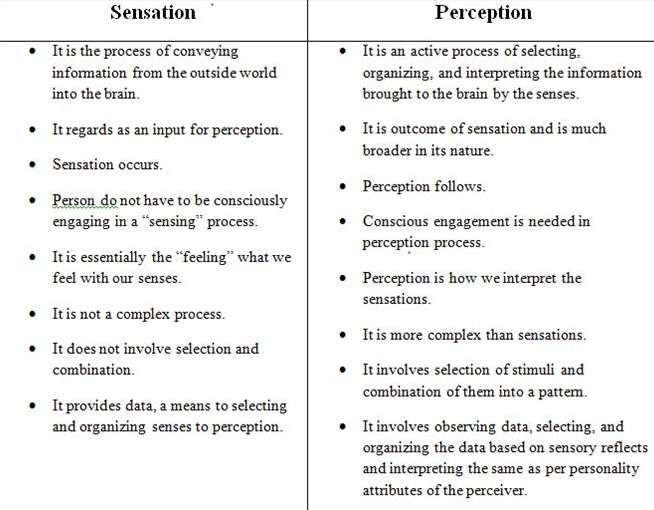
Perception is the process by which people select, organize and interpret sensory stimulus into meaningful information about their work environment. The knowledge is captured by interpreting the sensory input. Perception is more than sensory input supplied by sense organs and other receptors. It is the final product of raw and unprocessed sensations.
Definition by S.P. Robbins
| Perception is defined as the process by which an individual selects, organizes, and interprets information inputs to create a meaningful picture of the world. |
| Perception is a process by which an individual organizes and interprets their sensory impressions to give meaning to their environment. |
Feature of Perception:
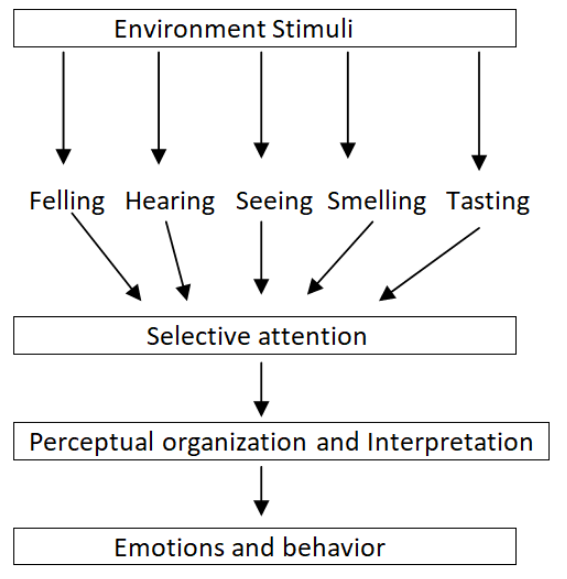
Perceptual Process(Model)
A Simple Model of the Perceptual Process:
The model has 3 variables: Input, Processes, and Output.
Inputs: Perceived inputs are the objectives, events, people that are received by the perceiver which begins when environmental stimuli are received by our five sense organs.
Processes: Input received is processed by this sub-process: Selection, organization, and interpretation.
Output: The output of perception can be seen in the form of behaviors and emotions. They may be the feelings, attitudes, actions, etc.
Perceptual errors: (frequently used shortcuts in judging others)
Perceptual errors are called when folks generally use several shortcuts when they judge others. They are:
OR
The perceptual process may result in a person making errors in judgment or understanding of another person. The most common types of perceptual errors are:
The tendency for people to protect themselves against ideas, objects, or situations that are threatening.
The belief that all members of a specific group share similar traits and behaviors.
A tendency to color everything we know about a person because of one recognizable favorable or unfavorable trait.
is the tendency to see one’s traits in others. The role of culture: Culture influence our perception in selecting information and exhibiting a behavioral pattern in situations
When the most recent information influences our judgment, even though we have a whole of other information on the person.
Based on one Negative quality, we assumed the person is BAD i.e. we perceived the whole person, based on ONE quality.
Ex- Rishi gets the best journalist award in Nepal but fails to get selected as the top 1000 journalists in South Asia. He attributes his success as his ability and his failure as a lack of capability of the judge to determine his ability.
People's preconceived expectations and beliefs determine their behavior, thus, serving to make their expectations come true. E.g. Negative expectations= Negative result
Factors affecting perception:
A perceived discrepancy between the current state of affairs and the desired state. Every decision problem requires selection, organization, and interpretation of information.
Every decision requires the development of alternatives. It also requires the development of relevant alternatives.
It is the selection of the best alternative. The final choice is influenced by the perception of the decision-maker.