Published by: Zaya
Published date: 16 Jun 2021

The situation prevailing in a market in which buyers and sellers are so numerous and well informed that all elements of monopoly are absent and the market price of a commodity is beyond the control of individual buyers and sellers are said to be perfect competition.
Characteristics
| Quantity | Price | Total Revenue | Average revenue | Marginal revenue |
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 10 |
| 3 | 10 | 30 | 10 | 10 |
| 4 | 10 | 40 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 10 | 50 | 10 | 10 |
| 6 | 10 | 60 | 10 | 10 |
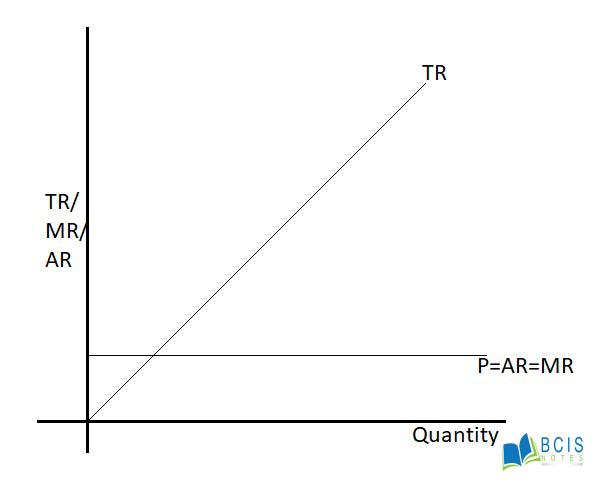
In the figure, TR is the total revenue curve. It begins from the origin which shows that total revenue is zero when quantity sold is nil. It moves upwards which means that total revenue increases when the quantity sold increases. AR is the average revenue or demand curve. It is a horizontal straight line parallel to the x-axis which indicates that price remains constant even if the quantity sold increases.
The situation prevailing in a market in which elements of monopoly allow individual producers or consumers to exercise some control over market prices is said to be imperfect competition.
Types:
2. Monopolistic Market
3. Oligopoly
| Output | Price | Total Revenue | Marginal revenue | Average revenue |
| 1 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 2 | 40 | 80 | 30 | 40 |
| 3 | 30 | 90 | 10 | 30 |
| 4 | 20 | 80 | -10 | 20 |
| 5 | 10 | 50 | -20 | 10 |
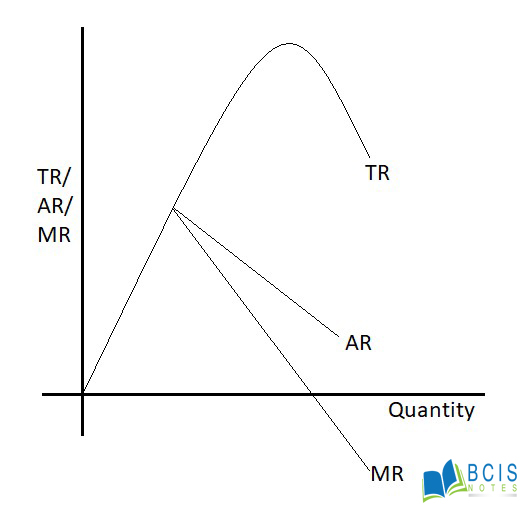
We measure, MR/AR/TR on the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis respectively.
In the above figure, TR is the total revenue curve, which passes through the origin, implying that TR is zero when the quantity sold is zero. The average revenue (AR) and marginal revenue (MR) are the downward sloping straight line.