Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021


US President Franklin D Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill met in the Atlantic Ocean and decided to prevent the world from any type of war and to maintain collective peace and security throughout the world. So, a treaty called ' Atlantic Charter' was signed in the Atlantic Ocean.
4 years after the treaty was signed, on 24th October 1945, 15 countries formally established UNO which headquarter is in New York, USA.
The UNO has 6 organs. They are:

Those agencies which are set up for a particular purpose or for a particular field are known as specialized agencies. The specialized agencies are working under the Economical and Social Council of the UN.
Some of the specialized agencies of the UN are:

The ILO was established on 11th April 1919. It was initially the agency of the League of Nations but it became a member of the UN after it was established. Its headquarter is in Geneva, Switzerland.
Functions:
i. It works for the welfare of laborers.
ii. It provides economic and social security to the labors.
iii. It helps in the formation of laws regarding the welfare of international laborers .iv. It makes plans and policies for the betterment of the labors and tries to control child labor.
 It was established on 16th October 1945 and its headquarter is in Rome, Italy.
It was established on 16th October 1945 and its headquarter is in Rome, Italy.
Functions:
i. It promotes food and agricultural products through effective measures.
ii. It helps in rural management to raise the living standard of people.
iii. It makes efforts to eliminate hunger throughout the world.

It was established on 4th November 1946 AD. Its headquarters is in Paris, France.
Functions:

It was established on 7th April 1948 and its headquarters is in Geneva, Switzerland.
Functions:
i. It helps to improve the general health of people around the world.
ii. It carries out researches regarding different diseases and in the field pf medical field.
iii. It provides vaccination to fight different epidemics and diseases in the world.

It is one of the specialized agencies of the UN which was established on 27th December 1945 in Washington DC, USA.
Functions:

It is a part of World Bank Group and was established on 27th December 1945 A.D. and the headquarters is in Washington, US.
Functions:

It was established as the International Telegraph Union on May 17, 1856, in Paris. Its headquarters is in Geneva, Switzerland.
Functions
i. It harmonizes telecommunication services throughout the world.
ii. It helps to expand telecommunication in rural areas.
iii. It makes an environment between countries regarding international phone calls,

It was established on 8th October 1874 but it became a specialized agency of UNO on July 1, 1948, and the headquarters is in Bern, Switzerland.
Functions:
i. It develops postal facilities worldwide.
ii. It fixes the postal rate for its member nations.
iii. It helps to find out the postal problems and recommend effective solutions.

It was established on 17th March 1958 with headquarters in London, UK.
Functions:
i. It works for the protection of sailors of the member nations.
ii. It promotes cooperation to improve maritime safety.
iii. It coordinates with member nations to reduce maritime pollution.
iv. It maintains cooperation regarding the use of international water resources.

It was founded on 22nd November 1965 and has been working in 166 countries with its head office in New York, USA.

It was formed on 1st January 1967 and its headquarters is in Vienna, Austria.
Functions:
i. It provides technical support for the industrial development of its member nations.
ii. It helps to develop mutual cooperation among the countries for industrial growth.
iii. It helps to build a good environment for trade and reduce poverty through productive methods.

It was established on 26th April 1970 and its headquarters is in Geneva, Switzerland.
Functions:
i. It protects intellectual property throughout the world.
ii. It signs different treaties regarding intellectual property protection.
iii. It is the contact point where copyrights, licenses are filed in multiple countries.

It was established on 30th November 1977 A.D. Its headquarters is in Rome, Italy.
Functions:
i. It encourages developing countries to invest in agriculture.
ii. It brings modernization in agriculture replacing the traditional methods.
iii. It provides employment to the farmers and a guaranteed market for their product.

It was founded on 7th December 1944 A.D and was established on 4th April 1947 but it became the agency of the UN in December 1947 with headquarters in Montreal, Canada.
Functions:
i. It sets the regulations for aviation safety and efficiency.
ii. It develops and saves international aviation.
iii. It provides obedience to international rules and cooperation in customs.

It was founded on 11th December 1946 A.D. in New York, USA.
Functions:
i. It protects child rights as well as takes care of women.
ii. It improves the health of children and develops their skills.
iii. It conducts various programs regarding nutrition, primary health care, and vaccination.
iv. It protects children from being tortured or exploited.
Activities of UNO

The number 66, with the blue plate and the flag of UNO, is the identification of the UN vehicle which might be on duty. UNO carries out various activities for the welfare of the people and the country in the world. It has been making several efforts for setting disputes around the world. 193 countries of the world are the member nations of UNO and have been employed about 65000 people under various programs on education, health, children peace, control of fatal disease, rescue program on emergencies, etc. the UNO spends over 8 billion US $ annually in carrying out the various activities for the human welfare in the world.
The required fund for the organization has been collected from the following sources:
i) It receives a donation from the member nations ranging from 0.001% to 30% on the basis of their economic status.
ii) The rich countries voluntarily donate the UNO to carry out various programs under it.
iii) The USA, the developed North American country donates about 30% fund for the UNO for launching various human welfare programs.
The collected fund is spent on the following activities launched by the UNO for the welfare of the people and the country in the world:
i) To bring out various programs to promote the living standard of the people in the world.
ii) It improves the socio-economic and political conditions of the member nations.
iii) It designs and carries out various activities to produce international cooperation, peace, and harmony.
iv) It brings various plans and programs to eradicate various problems and evils prevailing in the world.
v) It has been conducting programs to empower women in the world.
vi)It works for child rights, human rights, and brings various plans and policies to solve the problems faced by disabled, refugees, etc.
vii) It has been working to protect and preserve the world's natural and cultural heritage.
viii) It tries its best to preserve the environment from being polluted.

The specially trained and instructed task force that is sent to the war victim countries in the request of UNO to be a mediator between two rebels and to control the war temporarily is called Peace Keeping force. The peacekeeping force was established when Israel invaded Lebanon in 1978 A.D. The UN mobilizes the peacekeeping war victim nations in the world to maintain peace settling in the conflicts or disputes. The member nations of UNO can contribute by sending their national army and police to settle peace in war victim nations. Nepal also has been sending its troops as a peacekeeping force to Lebanon, Congo, Kosovo, Liberia, Haiti, Sudan, East Timor, etc. Recently the Nepalese peacekeeping force is working in Lebanon, Sudan, Haiti, and East Timor to settle the internal disputes of the nation.
Functions :
The UN peacekeeping force works under the direction and command of the head of the peacekeeping mission who has been appointed by the UN general assembly. The peacekeeping force wears the UN blue beret and their own army uniform when they are on duty. They are provided special and tactful training before going to the war victim nations. They are provided with modern weapons but they cannot use the weapons against the fractions there. They have the authority to use the weapons only for self-protection if required.
The following are the main duties and functions of peacekeeping force:
i) It protects both the warring factions from violence.
ii) It trains the national armies of the war victim nations.
iii) It helps in the construction of transport and other infrastructural development in the war victim nations.
iv) It helps to supply food items, medicines, and other required relief packages to the people of the war victim nations.
v) It clears mines and ambushes and makes safety for the local people.
vi) It supervises the local or national election and ensures the safety of the people in the election.
vii) It tries to maintain peace and order in the war victim nations through diplomatic efforts and negotiations.
The peacekeeping force consists of the following person:

UNMIN was established to help the peace process in Nepal. The UNMIN, the political mission was established on 23rd January 2007 A.D. under the leadership of Mr. Lan Martin. It stayed and helped Nepal for 4 years to establish permanent peace in Nepal. Its function came to an end on 15th January 2011 A.D. during the tenure of Karin Landgren. UNMIN is one of the missions sent by UNO for the restoration of peace and order in Nepal.
Roles played by UNMIN in Nepal
i) It played a vital role in managing arms and personnel of Maoist established in cantonment camps in various parts of the country.
ii. It continued its supervision to the activities of Maoist armies and armies of the Nepal government and their weapons stored in several cantonments and Nepal’s armies Chhauni Barrack.
iii) It played a great role to be the mediator between the Maoist and the government of Nepal to restore permanent peace in Nepal.
iv) It contributed to certifying and qualifying the Maoist army which helped to initiate the peace process in Nepal.
v) It tried its best to aware the Nepalese people about the activities of the peace process of the country through its radio program “Voice of UNMIN”
The other remarkable works of the UNMIN are as follows:
i) Monitor the management of arms and armed personnel of the Nepal Army and the Maoist army, in line with the provisions of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement.
ii) Assist the parties through a Joint Monitoring Coordinating Committee in implementing their agreement on the management of arms and armed personnel
iii) Assist in the monitoring of ceasefire arrangements
iv) Provide technical assistance to the Election Commission in the planning, preparation, and conduct of the election of a constituent assembly in a free and fair atmosphere.
v) It was expected that the mission would be liquidated in July 2009.to plan for this, UNMIN has gone two significant downsizing exercises, in July 2008 and January 2009. Staff strength has been reduced from 883 in January 2008, to 324 in October 2008 and 202 in July 2009. UNMIN also closed its five regional offices in July 2008.
vi) The Special Representatives of the Secretary-General leading the mission prior to the 2009 mandate renewal was Lan Martin. He gave his final briefing to the security council in January 2009 and was replaced by Karin Landgren. In 2009, the mandate was renewed, but with a phased withdrawal of UNMIN staff, in line with a report by the Secretary-General. In passing Resolution 1909 (2010), the Security council hoped to end UNMIN by May 15, 2010.
vii) UNMIN ceased operation on January 15, 2011.
The United Nations is an international founded in 1945 after the second world war by 51 countries committed maintaining international; peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations and promoting social progress, better living standards, and human rights. At present, it has 193 nations and its member. Its latest member nation is Montenegro. The general assembly first met in London on January 10, 1946. It decided to locate the UN headquarters in the eastern United States.
Due to its unique international character, and the powers vested in its founding charter, the organization can take action on a wide range of issues and provides a forum for its 193 member states to express their views through the general assembly, the security council, the economic and social council, and other bodies and committees.
The work of the united nations reaches every corner of the globe. Although best known for peacekeeping, peacebuilding, conflict prevention, and humanitarian assistance, there are many other ways the United Nations and its system affect our lives and make the world a better place. Nepal got the membership of UNO on 15th Dec. 1955 A.D. Since then she has agreed and signed the UN charter, treaties, commitment, resolution, and agreements. The specialized agencies of UNO are actively working for the welfare of Nepal and its citizen. It has been providing financial, technical, and another required assistant to promote and develop education, health, transport, communication, power etc.it has been supporting Nepal to preserve natural means and resources. It has been carrying out various plans to solve the problems prevailing in various societies of Nepal through its specialized agencies. It has been launching various plans and policies to raise the living standard of women, Dalit, indigenous tribes, physically retarded persons, and helpless people in Nepal since its establishment.
Montenegro is the 192nd member of the United Nations Organization. Now, UNO has a total of 193 members including the latest member nation Montenegro and Southern Sudan. The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was admitted as a member of the United Nations by General Assembly resolution on 1st November 2000. On 4th February 2003, following the adoption and promulgation of the constitutional charter of Serbia and Montenegro by the Assembly of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia “was changed to Serbia and Montenegro.” In a letter of date 3rd June 2006, the president of the Republic of Serbia and Montenegro was being continued by the Republic of Serbia, following Montenegro’s declaration of independence. Montenegro held a referendum on 21st May 2006 and declared its independence from Serbia on 3rd June 2006, it was accepted as the United Nations member State by the General Assembly.

The SAARC was officially established on December 8, 1985, for maintaining mutual cooperation among the South Asian countries. It is a non-political and regional organization comprised of seven members of the South Asian region earlier. Afghanistan joined the organization as the 8th member. So, now this organization has 8 member nations. Currently, SAARC has 9 observers. The logo of this organization was designed by Sailendra Maharjan, a citizen of Nepal. Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Nepal, Bhutan, Pakistan and Sri Lanka are the member nations of SAARC. Australia, China, European Union, Iran, Japan, Mauritius, Myanmar, South Korea, and the United States are the nine observers of SAARC.
i. Meeting of the Heads of States of government.
ii. Council of Ministers.
iii. Standing Committee.
iv. Technical Committee.
v. Action Committee.
vi. Secretariat.
i) To promote the welfare of the people of South Asian countries and develop their living standards and quality of life.
ii)To accelerate economic growth, social progress, and cultural development in the region and to provide all individuals the opportunities to live in dignity.
iii)To promote and strengthen collective self-reliance among the countries of South Asia.
iv)To cooperate with international and regional organizations with similar aims and purposes.
v)To contribute to mutual trust, understanding, and appreciation of one another are problems.
vi) To strengthen cooperation among themselves in international forums on matters of common interest.
vii) To promote active collaboration and mutual assistance in the economic, social, cultural, technical, and scientific fields, etc.
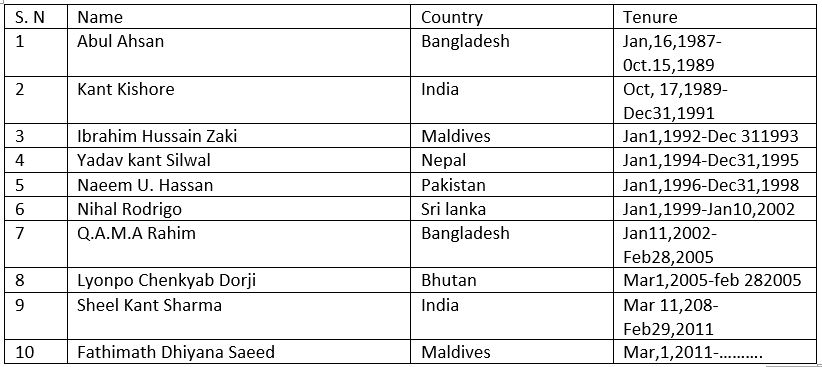
The SAARC Secretariat is the chief administrative body of SAARC which was established in Kathmandu on 16 January 1987. It coordinates and monitors the implementations of SAARC activities, services, and the meeting of the Association and serves as the channel of communication between SAARC and other international organizations. The Secretariat comprises the Secretary-General, seven Directors, and the general Services staff. The detail of its official and working divisions responsible for areas of work can be viewed under respective links. The chief administrator of SAARC is the General Secretary who is appointed by the council of Ministers for two years. India is the largest country to provide funds required for this organization. About 30% of the fund is given by India. The given table shows the General Secretaries of SAARC along with their respective countries and tenure of office.
1. First SAARC Summit, Dhaka, 1985
2. Second SAARC Summit, Bangalore, 1986
3. Third SAARC Summit, Kathmandu, 1987
4. Fourth Summit, Islamabad, 1988
5. Fifth SAARC Summit, Male', 1990
6. Sixth SAARC Summit, Colombo, 1991
7. Seventh SAARC Summit. Dhaka, 1993
8. Eighth SAARC Summit, New Delhi 1995
9. Ninth SAARC Summit, Male', 1997
10.Tenth SAARC Summit, Colombo, 1998
11. Eleventh SAARC Summit, Kathmandu, 2002
12. Twelfth SAARC Summit, Islamabad, 2004
13. Thirteenth SAARC Summit, Dhaka, 2005
14. Fourteenth SAARC Summit, New Delhi, 2007
15. Fifteenth SAARC Summit, Colombo, 2008
16. Sixteenth SAARC Summit, Thimphu, 2010
17. Seventeenth SAARC Summit, Addu City, 2011
18. Eighteenth SAARC Summit, Kathmandu, 2014.