Published by: Nuru
Published date: 06 Jul 2021

The United Nations held a Human Environment conference from June 5-16, 1972 in Stockholm, Sweden. This conference tried to draft a plan for Human Sustainability. In 1983, the UN approved to creation of a program for Environment and Development. As a result, Butland Commission was formed in the same year. This commission presented a paper on “Our Common Future” in the 42nd UN General Meeting in 1987. The paper defines Sustainable Development as: “Development that meets the need of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
Sustainable Development means searching for a direct balance between environment and development and finding the continued development criteria that the earth can support. In addition to that, development has to be done so that development in one area does not affect the development in another area.
1. It helps in the sustainable management of means and resources.
2. Create a better future for future generations.
3. Emphasizes on environmental conservation.
4. Obtains, utilizes, and conserves the means and resources available.
5. Handles fair distribution of means and resources.
6. Controls the over-utilization culture.
7. It helps in high and stable economic growth.
8. It helps to reduce, recycle, and reuse the main resources.
There are many factors for sustainable development. It is related to the social, cultural, economic, and human aspects of life. According to UNESCO, sustainable development depends on the social, economic, natural, and political aspects of a country. Social and cultural aspects include human community relations, cultural conservation, socio-cultural handovers, etc.
With the aim to complete a project within a certain time, using a certain amount of resources and implemented in a variety of well-organized manner for the development are generalized as development projects. Development projects are small or large depending on the goals, investments, expected results, affected area, etc. Some projects are implemented at the local level, some in the state level, and some in the national level. National projects are organized if the project benefits the majority of people in the country and represents the national identity. National level projects require more resources and investment as compared to the regional and local level projects. These development projects have been renamed as Development Projects for National Pride. As of 2073 BS, there are 21 development projects for national pride. Such projects are added or removed with time.
Some development projects ongoing in Nepal are:
Apart from these above-mentioned projects, various National Pride Projects are being run. Some of them are Koshi, KaliGandaki and Karnali Corridor, Hulaki Sadak, Kathmandu-Terai Fast Track, East-West Electrical Railway, Melamchi Drinking Water, Gautam Buddha International Airport, Nijgadh International Airport, Pashupati Area Development Fund, Lumbini Development Fund, West Seti Electricity Project, Bheri-Babai Diversion Multi-Purpose Project, etc.
Most essential things or services which are required for social, economic, cultural, development, to raise the living standard of the people is termed as infrastructures. For example education, transportation, communication etc.
Nature gifted things that are available in nature and used to carry out development activities are known as natural resources. Air, water, minerals, etc are some of the examples of Natural Resources.
Means and Resources are those things that are man-made (artificial) or natural and are utilized to perform development activities that are known as means and resources. Capital, Skilled human resources come under artificial and air, water comes under natural means and resources.
From education, we learn knowledge, skills, and aptitude and from training, we get skills associated with efficiency. And with education and training, a person with capacity, positive thinking, and willingness to work is called a skilled person. Skilled manpower means engineers, doctors, teachers, alumni plans, nurses, and more. Construction of any national development planning and implementation requires skilled manpower. World's developed countries are developed because of the adequate availability of skilled manpower. Developing countries often lack resources and skilled manpower resources and the mobilization of them is a substantial problem. Therefore these countries must seek compatibility with the country and prioritize education and produce skilled manpower.
Well-educated, dedicated, and skilled individuals easily get employment opportunities. The country aims to citizens to make them educated and skilled so they get employment opportunities. Educational institutions and training centers supply the country with skilled manpower according to the market demand, and the country's skilled manpower requirement. The skilled manpower not only seeks employment but also creates entrepreneurial independent opportunities. The country has to create opportunities for skilled manpower to work or self-employ them to utilize their skills. Only then is it possible for a country to develop? It is always better if an individual can utilize their skills in the country itself, rather than search for opportunities abroad.
Development is always planned. It is the first condition for effective planning and development. The local and national-level action plan is developed after planning. Development planning is also a skill. Formulating a plan for the appropriate use of available resources and means to fulfill certain objectives in the specified period is called Development Proposal Formulation. What is done in this? Why is it done? Who does it? How is it done? Where is it done? When is it done? The answer to these questions is presented in the proposal. The preparation of these development plans is also said to be the first step in the development process.
The countries that have adopted federalism or decentralized government assign the local level offices to freely formulate and implement the development plans. The use of local means and resources, decisions on development works, and conduction of those works are given to the local offices. Consumer groups are created in the local community to include the locals in the development works. The local level development works are done by those consumer groups. Before formulating development plans requirements need to be assessed and selected, planned, investment selected, involvement decided, and means and resources availability checked. The proposed plans are then decided upon and then the development work is started.
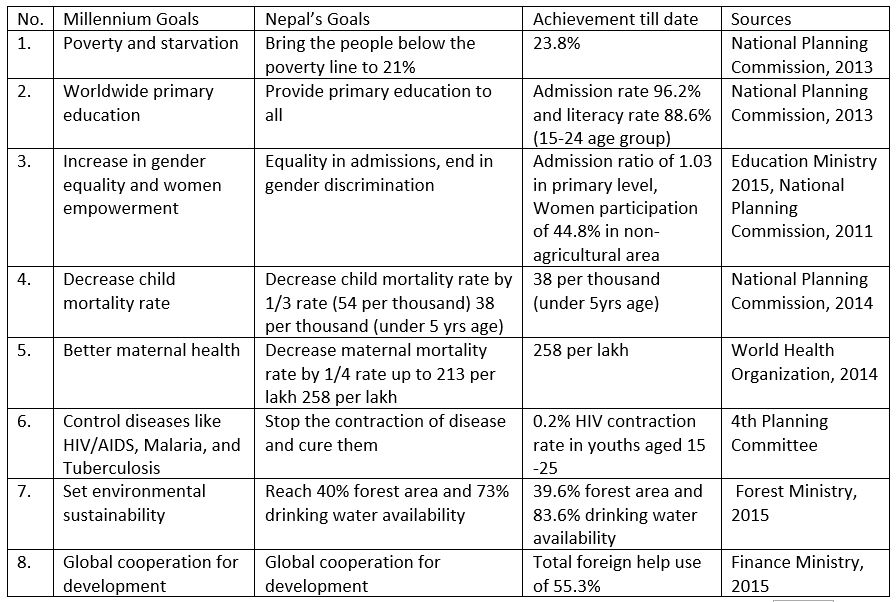
The UN General Assembly of 1990 formulated the goals for Eradication of Poverty. In September of 2000, the Millennium Development Goals was announced. This paved the way for developing countries to eradicate economic and human poverty. It listed the 8 goals and 21 points that needed to be done from 1990 to 2015. 189 countries along with Nepal signed the paper.
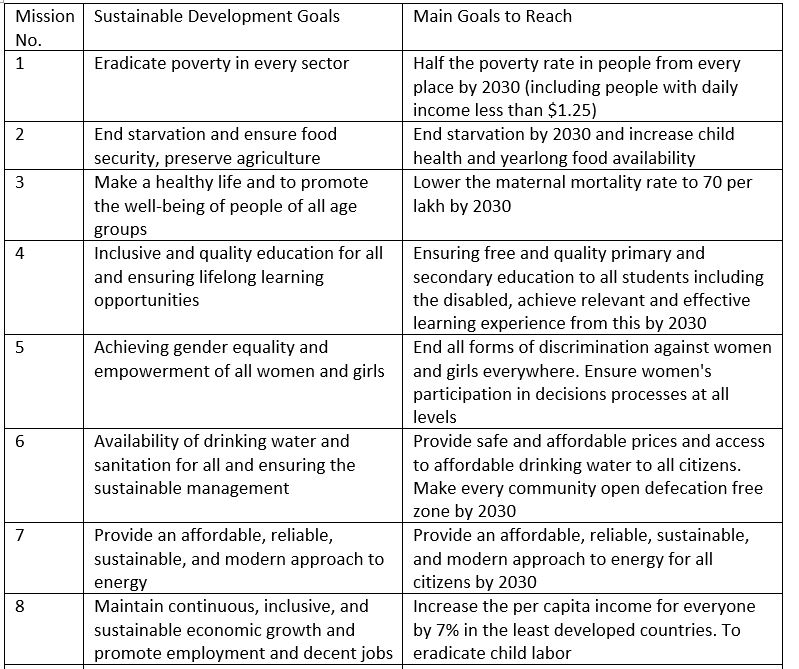
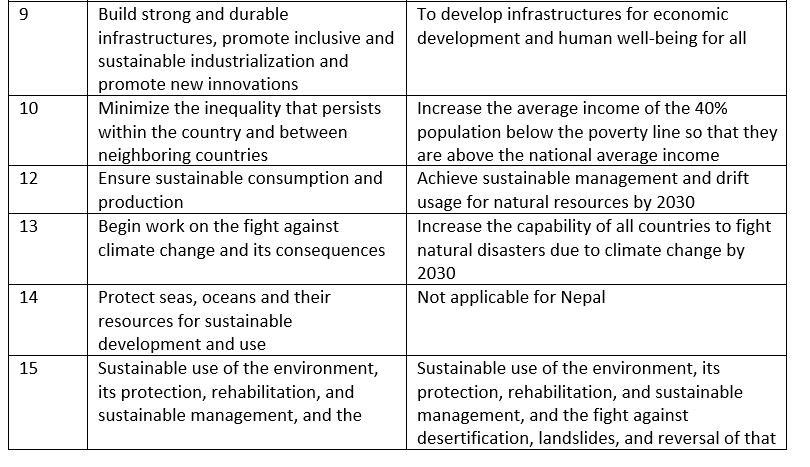
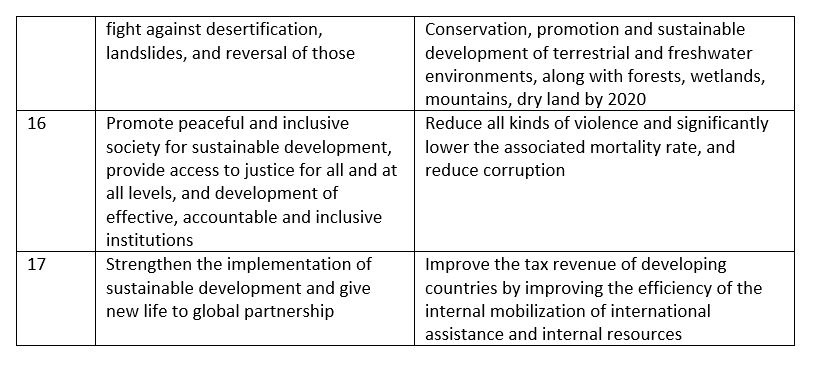
Sustainable development goals have been a topic of discussion for more than two decades. Its official beginning has been since June 2012 in Rio De Janerio and September 2014 in UN General Assembly. The millennial goals ended in 2015 and this has been the plan from 2015 to 2030. The 2015 September assembly accepted the goals and put them into work. There are still missing some index points and program plans. There are 17 goals and 169 destination points declared up to this point in time.
Nepal has the goal of improving its rank from developing nations to an upper level. These goals are very vast, with great expectations and very demanding which requires much means and resources. By 2030, Nepal has goals to be an inclusive, peaceful country with an average income for its citizens.