Published by: Sujan
Published date: 18 Jun 2021
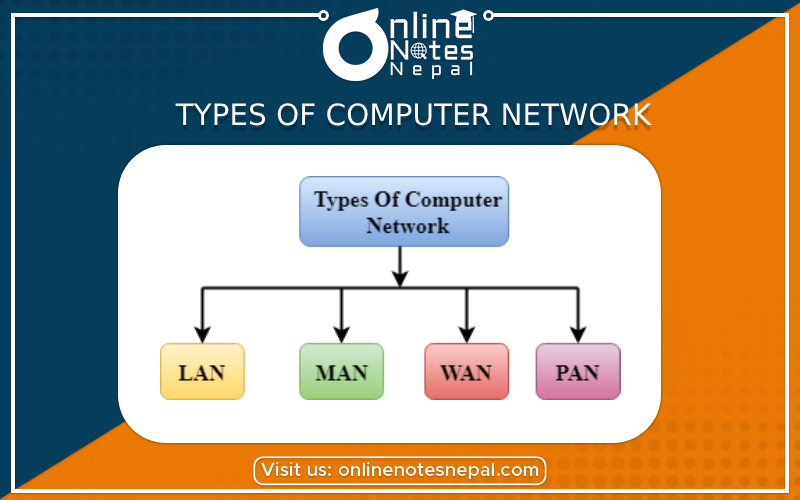
A computer network is an interconnection of two or more computers that are able to exchange information. The computers may be connected via any data communication link, like copper wires, optical fibers, communication satellites, or radio links. The computers in a network may be located in a room, building, city, country, or anywhere in the world.
Network Types
A computer network is broadly classified into three types: —
LAN is a type of computer network widely used for local communication. LAN connects computers in a small area like a room, building, office or a campus spread up to a few kilometers. They are privately-owned networks, with a purpose to share resources and to exchange information.
some of the features of LAN are:
• The computers in a LAN are generally connected using cables.
• Some of the transmission protocols used in LAN are Ethernet, Token Bus, and FDDI ring.
• Star, Bus, and Ring are some of the common LAN networking topologies.
• LAN runs at a speed of 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps and has low delays
{PHOTO}
MAN is a typical computer network spread over a city. The cable television network is an example of a MAN. The computers in a MAN are connected using coaxial cables or fiber optic cables.MAN also connects several LAN spread over a city.
WAN is a type of computer network that connects computers over long distances like cities, countries, continents , or worldwide . WAN uses public, leased, or private communication links to spread over long distances. WAN uses telephone lines, satellite link, and radio link to connect. The Internet is a common example of WAN.
{PHOTO}
The network topologies is the structure or the layout of the different devices and computers connected to the network.
The topologies commonly used in LAN are:—
• Bus topology
• Ring topology
• Star topology
• Tree topology
Bus Topology
All devices on the network are connected through a central cable called a Bus.
{PHOTO}
Merits of Bus Topology
• It is cost-effective.
• Used in small networks.
• Use less cabling.
• Easy to understand & use.
• Easy to add new nodes(computer) in network.
Demerits of Bus Topology
• Data collision is high.
• All network shut down if cable fails.
• Difficult to find fault.
• Cable has a limited length.
• Slower than ring topology.
{PHOTO}
All devices in the network are connected in the form of a ring. Each device has a receiver and transmitter to receive the data signals and to send them to the next computer, respectively. Ring network does not have terminated ends, thus data signals travel in a circle. Ring topology uses a token passing method to provide access to the devices in the network.
Merits of Ring Topology
• No much traffic problem.
• Very high transmission speed possible.
• Small cable segments are needed to connect two nodes.
Demerits of Ring Topology
• Failure of any one node(computer) makes whole network down.
• Very hard to find error.
• Adding & removing the nodes disturbs the network activity.
{PHOTO}
All devices are connected through a central link forming a star-like structure. The central link is a hub or switch. The computers are connected to the hub or switch using twisted pair cables, coaxial cables or optic fibers. Star topology is the most popular topology to connect computer and devices in the network. The data signal is transmitted from the source computer to the destination computer via the hub or switch.
Merits of Star Topology
• Easy to install & modify.
• Easy to find fault.
• Fast performance & low network traffic.
• Only one node is affected which has failed the rest of nodes can work.
Demerits of Star Topology
• Dependent on root.
• Failure of central hub/switch makes the whole network down.
• More cabling is used.
• Expensive to use.