Published by: Sujan
Published date: 18 Jun 2021
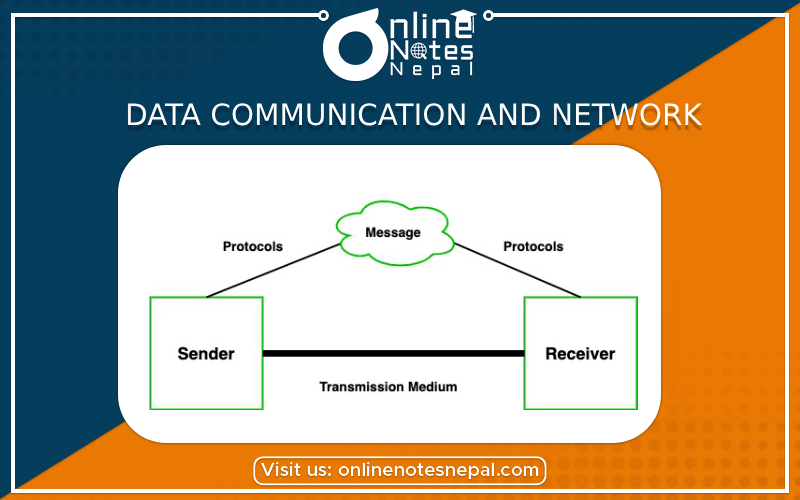
Data Communication and Network at the physical level involves the hardware required for handling individual bits and encoding bits in signals. Any two devices directly linked via a communication medium (point to point communication) can send and receive data, to and from each other respectively.
If a large number of computers need to interact with each other, point to point communication will require a direct link between all the computers.
For long-distance communication, instead of point to point connection, a network of nodes is used as a communication medium.
{PHOTO}
Switching
Networks allow the sharing of communication medium using switching.
Switching routes, the traffic (data traffic) on the network.
It sets up temporary connections between the network nodes to facilitate the sending of data.
Switching allows different users, fair access to the shared medium.
There are three kinds of switching techniques: —
Computer networks generally use packet switching, occasionally use circuit switching but do not use message switching.
Circuit Switching
Circuit switching sets up an end-to-end communication path between the source and the destination before the data can be sent.
The path gets reserved during the duration of the connection. Circuit switching is commonly used in the telephone communication network.
{PHOTO}
Message Switching
Message switching does not establish a physical path in advance, between the sender and the receiver. It uses the ‘store and forwards’ mechanism. In this mechanism, the network nodes have large memory storage. Message switching requires large data storage capacity and cause a delay in storing and forwarding of a message.
Message switching may block the network nodes for a long time. They are thus not suitable for interactive communication. Message switching is no more used in computer networks.
{PHOTO}
Packet Switching
Like message switching, packet switching does not establish a physical path between the sender and the receiver, in advance. Packet switching also uses the ‘store and forward’ mechanism. Packet switching splits a message into small “packets” of defined size to be sent over the network.
{PHOTO}