Published by: Dikshya
Published date: 28 Jul 2023
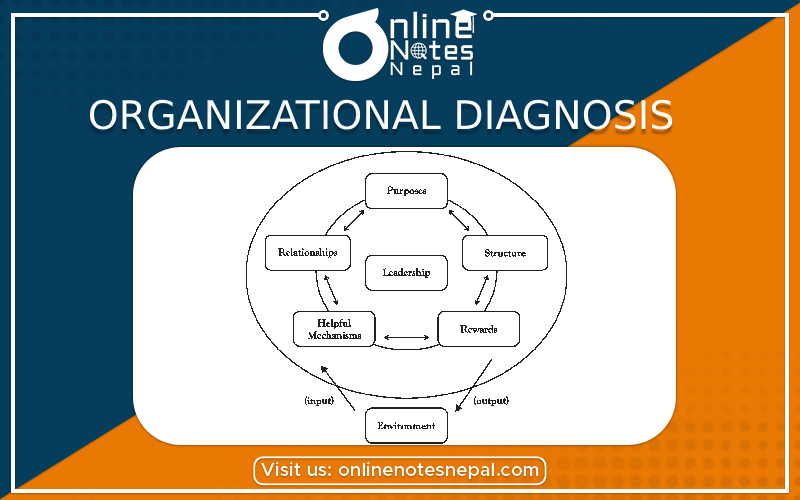
Introduction:
Organizational diagnosis is a systematic approach used by businesses and consultants to analyze and assess the health, functioning, and overall performance of an organization. It is a critical process that provides valuable insights into an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Through organizational diagnosis, leaders can identify areas for improvement, design effective interventions, and implement changes to enhance productivity, efficiency, and employee satisfaction.
1. Purpose of Organizational Diagnosis:
The primary purpose of organizational diagnosis is to gain an in-depth understanding of an organization's structure, culture, processes, and performance metrics. By conducting this diagnosis, leaders can achieve the following objectives:
a. Identify Issues: Pinpoint underlying issues and challenges that hinder organizational growth and effectiveness.
b. Improve Efficiency: Identify inefficiencies and streamline processes to optimize resource allocation and enhance productivity.
c. Enhance Communication: Evaluate communication patterns and foster open communication channels within the organization.
d. Strengthen Culture: Assess organizational culture and values, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives.
e. Enhance Employee Engagement: Understand employee satisfaction, motivation, and well-being, leading to better engagement and retention.
f. Adaptation to Change: Determine the organization's capacity to adapt to external changes, such as technological advancements or market trends.
2. Steps in Organizational Diagnosis:
a. Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from various sources, such as interviews, surveys, observations, and existing documents, to create a comprehensive picture of the organization.
b. Data Analysis: Analyzing the collected data to identify patterns, trends, and potential problem areas.
c. Diagnostic Models: Utilizing established diagnostic models, such as the 7S Framework, SWOT analysis, or McKinsey's 7 Elements, to structure the diagnosis and provide a framework for analysis.
d. Stakeholder Involvement: Involving key stakeholders at all levels of the organization to ensure a holistic understanding of the organization's dynamics and culture.
e. Feedback and Communication: Presenting the findings to relevant stakeholders and promoting open dialogue to generate consensus on areas for improvement.
f. Intervention Design: Collaboratively developing action plans and interventions to address identified issues and capitalize on opportunities.
g. Implementation: Executing the interventions and monitoring their effectiveness over time.
3. Types of Organizational Diagnosis:
a. Strategic Diagnosis: Focuses on evaluating the alignment between the organization's mission, vision, and strategic objectives with its actual practices.
b. Structural Diagnosis: Analyzes the organization's formal structure, hierarchy, and reporting lines to ensure efficiency and effectiveness.
c. Cultural Diagnosis: Examines the organization's shared values, norms, and beliefs to determine if the culture supports or hinders performance.
d. Human Resources Diagnosis: Assesses HR processes, policies, and practices, including recruitment, training, and performance management, to optimize talent management.
e. Technological Diagnosis: Evaluates the organization's technological infrastructure and its impact on productivity and innovation.
4. Benefits of Organizational Diagnosis:
a. Enhanced Performance: By identifying and addressing weaknesses, organizations can enhance overall performance and achieve their strategic goals more effectively.
b. Employee Engagement: Diagnosis helps identify factors that impact employee engagement, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction and motivation.
c. Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights enable leaders to make informed decisions, reducing risks associated with change initiatives.
d. Effective Change Management: Organizations can implement changes more smoothly and successfully with a clear understanding of their strengths and weaknesses.
e. Competitive Advantage: By continuously diagnosing and improving, organizations can gain a competitive edge in their industry.
Conclusion:
Organizational diagnosis is a crucial tool for leaders and consultants seeking to understand and enhance organizational performance. By assessing various aspects of the organization, leaders can identify areas for improvement and design effective interventions to promote long-term success. Regularly conducting organizational diagnosis allows businesses to adapt to changing environments, foster employee engagement, and maintain a competitive advantage in today's dynamic and challenging market.