Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jan 2022
Nepal is commonly divided into three physiographic areas; Mountain, Hill, and Terai. These ecological structures run east-west and are vertically intersected by Nepal's major, north to south flowing river systems. Nepal is separated from Bangladesh by the narrow Indian Siliguri, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Kathmandu is the capital city of the country.
The state is a commodity of the people, occupying a definite territory, organized under the government which is supreme of all persons within the territory. To form a state, people must be organized under a government. It should also have a fair number of people living within the boundary. A state has its own government.
The government in the state is free from any external controls. The people in a state are politically organized. In general, the state is a recognizable geographical area that is composed of people, definite territory, government, and sovereignty. Leaders of political parties have finally agreed to federate the country into six states. The decision was agreed by four major parties in the Special Committee on the Constituent Assembly’s Constitutional Committee. This certainly is a breakthrough in the constitution drafting process and the Prime Minister Sushil Koirala has asserted that the country would get a new constitution soon after the agreement.
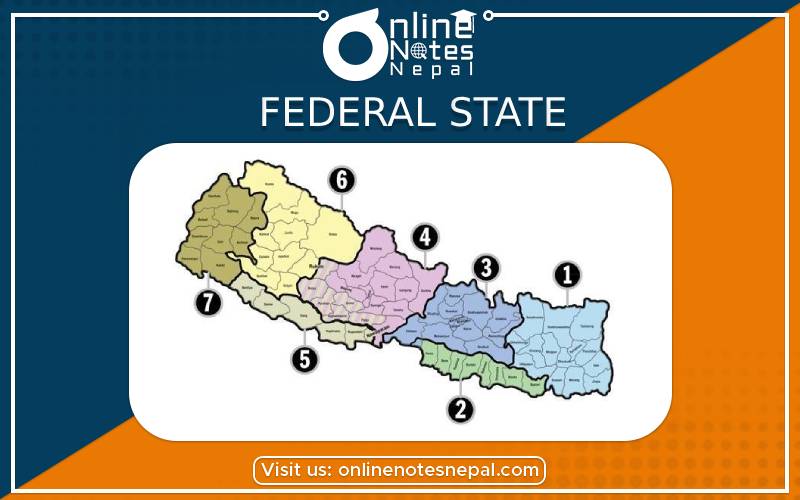
a. State 1: Taplejung, Panchthar, Ilam, Jhapa, Morang, Sunsari, Udaipur, Dhankuta, Terhathum, Sankhuwasabha, Solukhumbu, Bhojpur, Khotang and Okhaldhunga.
b. State 2: Saptari, Siraha, Dhanusha, Mahottari, Sarlahi, Rautahat, Bara and Parsa.
c. State 3: Makwanpur, Chitwan, Sindhuli, Ramechhap, Dolakha, Kathmandu, Bhaktapur, Lalitpur, Kavre, Sindhupalchok, Rasuwa, Nuwakot, and Dhading.
d. State 4: Gorkha, Lamjung, Kaski, Tanahun, Baglung, Manang, Mustang, Myagdi, Syanjga, Parbat and Nawalparasi (From Daunne to Susta).
e. State 5: Kapilvastu, Rupandehi, Nawalparasi (Western region), Palpa, Argakhanchi, Gulmi, Dang, Pyuthan, Salyan, Rukum, Rolpa, Banke and Bardiya.
f. State 6: Kailali, Kanchanpur, Doti, Achhan, Bajura, Dadeldhura, Bajhang, Baitadi, Darchula, Humla, Dolpa, Mugu, Kalikot, Jumla, Dailekh, Surkhet and Jajarkot.
A Government is the group of people that governs a community or unit. It is the system by which a state or community is controlled. It is an agency through which the state formulates its plans and policies.
The government is the means by which state policy is enforced. The government is also needed to utilize natural resources, environmental protection, national defense, security, and foreign affairs. The government of any kind currently affects every human activity in many important ways.
An organization of the population living in the same group or species of a particular geographical area constitutes a state. The state is a human institution. So, a population is its primary element. There is no hard and fast rule about population. There is no definite number of people required to be a state. But it should be large enough to be self-sufficient.
The permanent population of the state is called citizens. However, a large population can be a liability if the resources of the state are not adequate for its maintenance. One of the main problems faced by developing countries is over-population.
A definite and more or less permanent territory is also regarded as an essential element of the state. In modern times, the citizens are bound together by a residence on a common territory. Land, water, and airspace comprise the territory of a state. Any geographical area owned and controlled by the government of a state is called territory.
It is a geographical area needed for the state to exercise its functions. It may be pointed out that the power and security of a state are not determined only by the size of its territory. Some other factors in this regard are geographical location, resources, and climate.
The word sovereignty is sometimes understood as 'independence'. It is also the quality of having supreme, independent authority over the territory. Sovereignty has two aspects internal and external. Internally viewed, the state has supreme power over all individuals and associations within its fixed area.
It can compel the obedience of its people to its laws and commands. Externally viewed, the state is free from the control of any foreign state or alien rule. In a democratic country, people are considered to have sovereign power. In a monarchy, sovereignty rests in an institution, and in a dictatorship, it is in the hand of a single person.