Published by: Sareena Kumari Basnet
Published date: 24 Jul 2024

A relational database is a type of database. It uses a structure that allows us to identify and access data in relation to another piece of data in the database. Often, data in a relational database is organized into tables.
A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a program that allows you to create, update, and administer a relational database. Most relational database management systems use the SQL language to access the database. MySQL, SQL-Server, MS-Access, Oracle are some of popular RDBMS.
Examples of RDBMS structure:
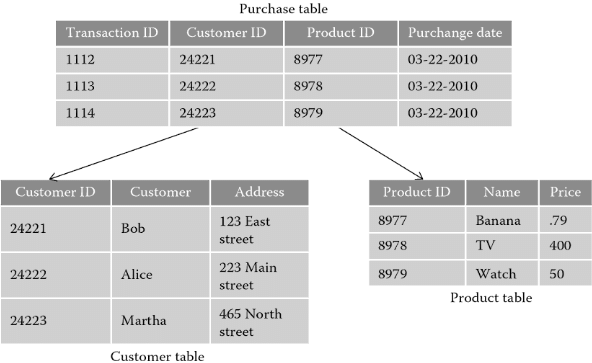
A database schema can be divided broadly into two categories -
 Keys
KeysA DBMS key is an attribute or set of an attribute which helps you to identify a row(tuple) in a relation(table). They allow you to find the relation between two tables. Keys help you uniquely identify a row in a table by a combination of one or more columns in that table.
A superkey is a group of single or multiple keys which identifies rows in a table. A Super key may have additional attributes that are not needed for unique identification.

In the above-given example, EmpSSN and EmpNum name are superkeys.
Rules for defining Primary key:
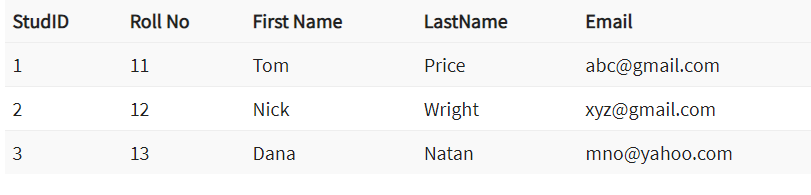
Here, Studid is a Primary Key.
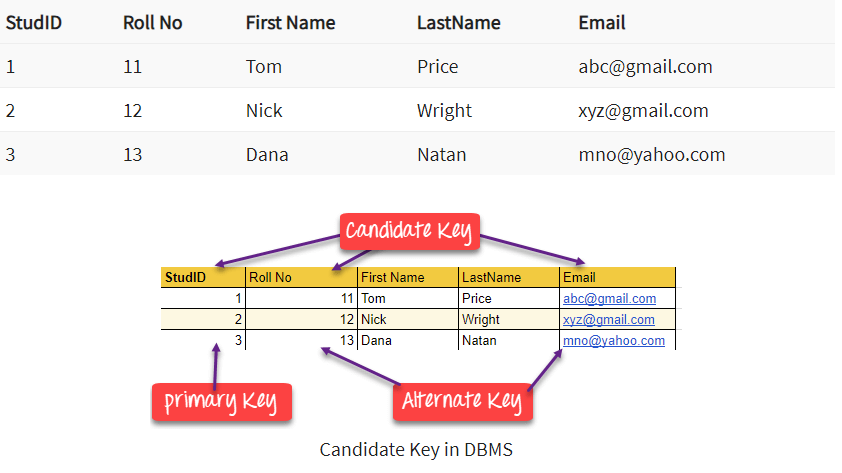
Candidate Key in SQL is a set of attributes that uniquely identify tuples in a table. Candidate Key is a super key with no repeated attributes. The Primary key should be selected from the candidate keys. Every table must have at least a single candidate key. A table can have multiple candidate keys but only a single primary key.
Properties of Candidate key:
Example: In the given table Stud ID, Roll No, and email are candidate keys which help us to uniquely identify the student record in the table.
Foreign key is a column that creates a relationship between two tables. The purpose of Foreign keys is to maintain data integrity and allow navigation between two different instances of an entity. It acts as a cross-reference between two tables as it references the primary key of another table.
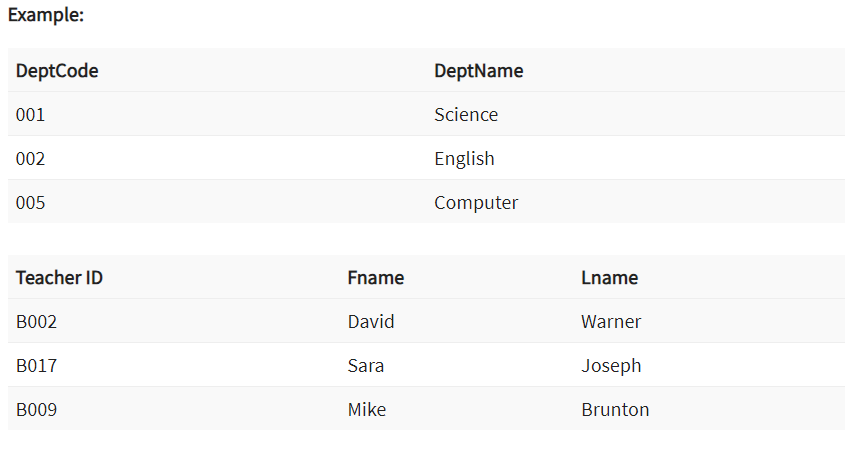
In this key in dbms example, we have two table, teach and department in a school. However, there is no way to see which search work in which department.
In this table, adding the foreign key in Deptcode to the Teacher name, we can create a relationship between the two tables.
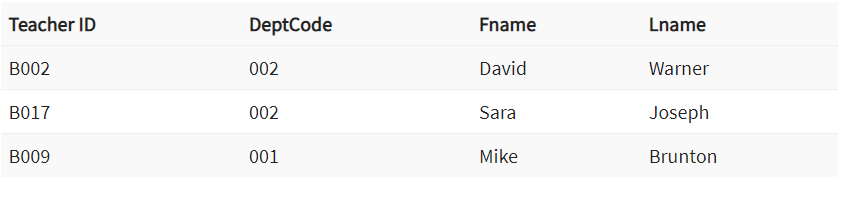
Composite Key is a combination of two or more columns that uniquely identify rows in a table. The combination of columns guarantees uniqueness, though individually uniqueness is not guaranteed. Hence, they are combined to uniquely identify records in a table.
The difference between compound and the composite key is that any part of the compound key can be a foreign key, but the composite key may or maybe not a part of the foreign key.
There may be one or more attributes or a combination of attributes that uniquely identify each tuple in a relation. These attributes or combinations of the attributes are called the candidate keys. One key is chosen as the primary key from these candidate keys, and the remaining candidate key, if it exists, is termed the alternate key. In other words, the total number of the alternate keys is the total number of candidate keys minus the primary key. The alternate key may or may not exist. If there is only one candidate key in a relation, it does not have an alternate key.
For example, employee relation has two attributes, Employee_Id and PAN_No, that act as candidate keys. In this relation, Employee_Id is chosen as the primary key, so the other candidate key, PAN_No, acts as the Alternate key.

