Published by: Zaya
Published date: 18 Jun 2021
Data communication refers to the exchange of data between a source and a receiver via form of transmission media such as a wire cable. Data communication is said to be local if communicating devices are in the same building or a similarly restricted geographical area.
Electronic communications, like emails and instant messages, as well as phone calls are examples of data communications.
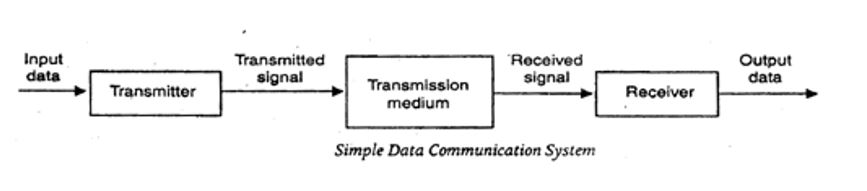
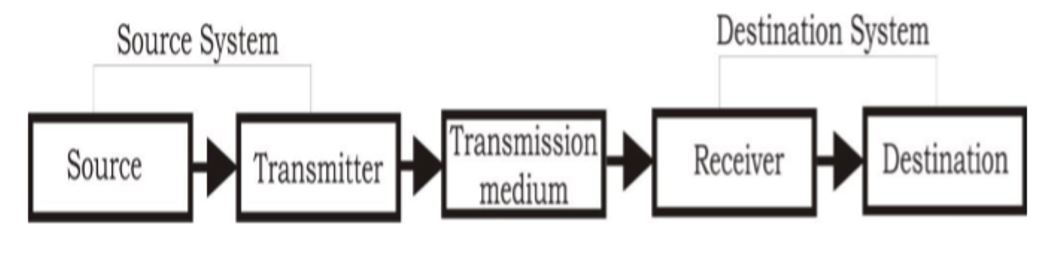
Above figure shows the basic block diagram of a typical data communication system. This can further be broken down to three; the source system, transmission system and destination system.
The source generates the information or data that will be transmitted to the destination. Popular forms of information include text, numbers, pictures, audio, video or a combination of any of these.
The transmitter a device used to convert the data as per the destination requirement.
For example a modem, converts the analog (telephonic) signal to digital (computer) signals and alternatively digital to analog.
The transmission medium is the physical path by which data travels from transmitter to receiver.
For Example of such channels is copper wires, optical fibers and wireless communication channels etc.
This receives the signals from the transmission medium and converts it into a form that is suitable to the destination device.
For example, a modem accepts analog signal from a transmission channel and transforms it into digital bit stream which is acceptable by computer system.
It is simply a device for which source device sends the data.