Published by: Zaya
Published date: 18 Jun 2021
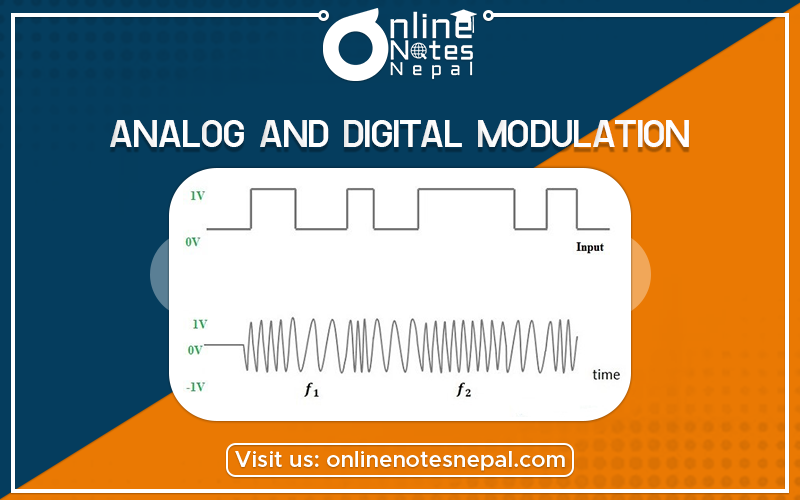
Analog and digital modulation are described below:-
The term DM stands for digital modulation, and it is a common term for the techniques of modulation. This modulation uses discrete signals for modulating a carrier wave. Indifference, both the amplitude modulation and frequency modulation techniques are analog. It removes communication noise as well as provides enhanced strength for signal intrusion. But, it is not rare to it schemes for introducing time delay because of the required process. To avoid this, a comfortable SST (Secure Stream Technology) audio is designed.
Types
There are several kinds of digital modulation techniques are available based on the requirement which includes the following.
• ASK or Amplitude shift Key
• FSK or Frequency shift key
• PSK or Phase shift key.
1) ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying)
In amplitude shift keying, once the instant amplitude of the carrier signal is changed in quantity toward m(t) message signal. For instance, if we have the modulated carrier (m(t) coswct) then the carrier signal will be coswct. Because the data is an ON/OFF signal, and the output is also an ON/OFF signal wherever the carrier is there when data is 1, as well as the carrier, is not present when data is 0. Therefore this modulation scheme is called OOK or on/off keying (OOK) otherwise amplitude shift keying or ASK. The applications of ASK mainly include IR remote controls and fiber optic transmitter & receiver.
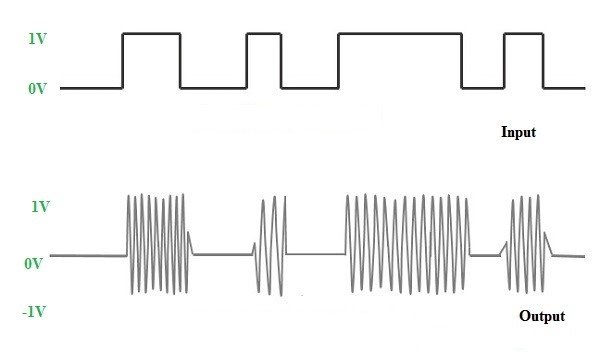
fig:-Amplitude Shift Keying
2) FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)
In frequency-shift keying, when the immediate frequency of the carrier signal is changed then the information will be transmitted. In this type of modulation, carrier signal has two pre-defined frequencies namely wc1, and wc2. Whenever the data bit is ‘1’ then the carrier signal by wc1 is transmitted that is coswc1. Similarly, when the data bit is ‘0’ then the carrier signal by wc0 will be transmitted that is coswc0. The applications of frequency shift keying mainly include several modems in telemetry systems and phase shift keying.
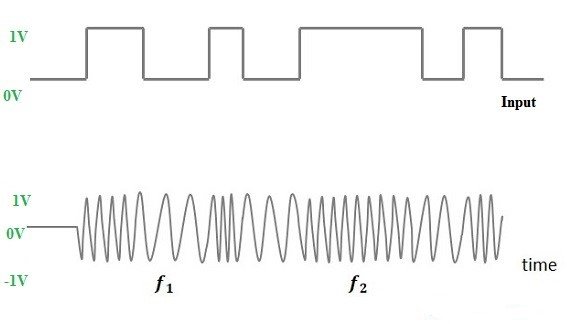
fig:-Frequency Shift Keying
3) PSK Digital Modulation(Phase Shift Keying)
In phase-shift keying, the instant phase of the carrier signal is moved for this modulation. If the m(t) baseband signal is =1 then the carrier signal within phase will be transmitted. Similarly, If the baseband signal m(t)=0 then the carrier signal by out of phase is transmitted that is cos(wct+П). If phase shift can be done in four dissimilar quadrants then 2-bit of data will be transmitted at once. This method is an individual case of phase-shift keying modulation which is known as Quadrature Phase Shift Keying or QPSK. The applications of phase-shift keying include a broadband modem (ADSL), satellite communications, mobile phones, etc.
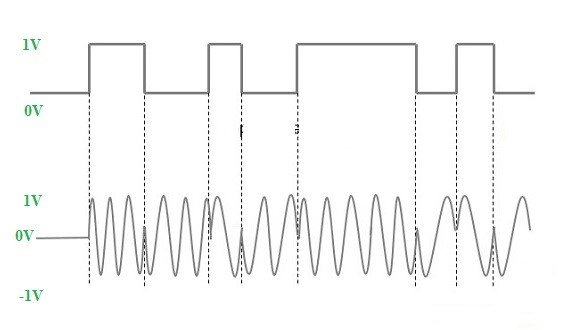
fig:-Phase Shift Keying
In analog modulation, an analog signal (sinusoidal signal) is used as a carrier signal that modulates the message signal or data signal. The general function of Sinusoidal waves are shown in the figure below, in which, three parameters can be altered to get modulation – they are amplitude, frequency, and phase; so, the types of analog modulation are:
• Amplitude Modulation (AM)
• Frequency Modulation (FM)
• Phase Modulation (PM)