Published by: Anu Poudeli
Published date: 02 Aug 2023
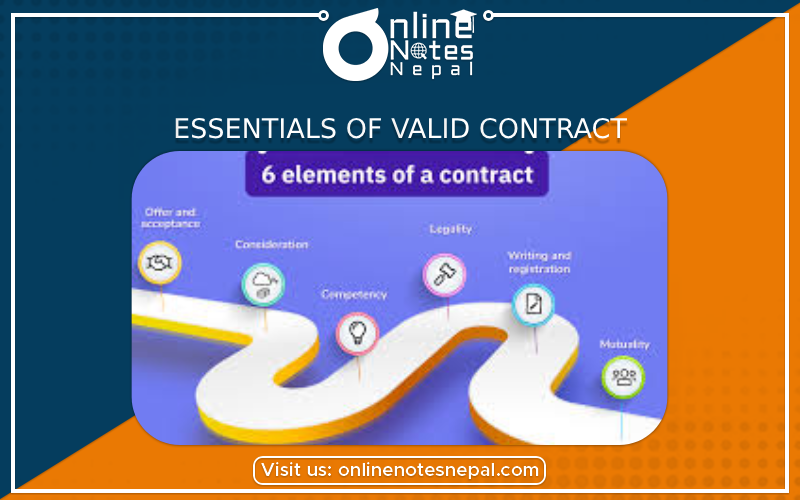
A legitimate contract is a legally enforceable agreement that generates mutual duties between two or more parties. Certain basic factors must be present for a contract to be legally enforceable. Understanding these factors is critical to ensuring that the contract is legitimate and will stand up in court.
The following are the key elements of a legal contract:
1.Offer and Acceptance: A legal contract begins with one party making a clear and unequivocal offer to another. The offer must be communicated to the other party and accepted without conditions or changes. The acceptance must be communicated back to the offeror, resulting in a mutual understanding between the parties.
2.Intention to Establish Legal Relations: The parties to the contract must intend to be legally bound by the terms of the agreement. Social agreements, casual commitments, or joking agreements are not usually considered legally binding contracts.
3.Consideration: A consideration is something of value that each party must exchange in order for the contract to be enforceable. Money, products, services, or a commitment to do or not do anything could all be considered. For the contract to be legal, both parties must provide some form of consideration.
4.Capacity: All parties engaging into the contract must be legally capable of doing so. This means they must be of sound mind, of legal age (adults), and not under the influence of any factors that would impair their decision-making abilities.
5.Lawful object : The subject substance of the contract, as well as the purpose for which it is made, must be lawful. Contracts made for illicit activity or with illegal goals are not valid and are void ab initio (invalid from the start).
6.Free Consent: The parties must enter into the contract freely and voluntarily, without force, fraud, misrepresentation, or undue influence. If approval is gained in this manner, the contract may be voidable at the discretion of the affected party.
7.Certainty and Performance Possibility: The contract's terms and conditions must be sufficiently clear and specific so that both parties understand their respective obligations. Furthermore, the contract must be performable; otherwise, it would be ruled void.
8.Writing and Registration : While most contracts can be oral or inferred, many types of contracts must be in writing to be enforceable. Furthermore, some contracts, particularly those involving real estate, may necessitate registration with the right authorities.
When drafting or entering into a contract, it is critical to verify that all of these factors are present and followed. Failure to meet any of these standards may declare the contract null and void. Seeking legal counsel and help, particularly for complex or substantial contracts, is suggested to secure their validity and defend the interests of all parties involved.