Published by: Nuru
Published date: 21 Jun 2021
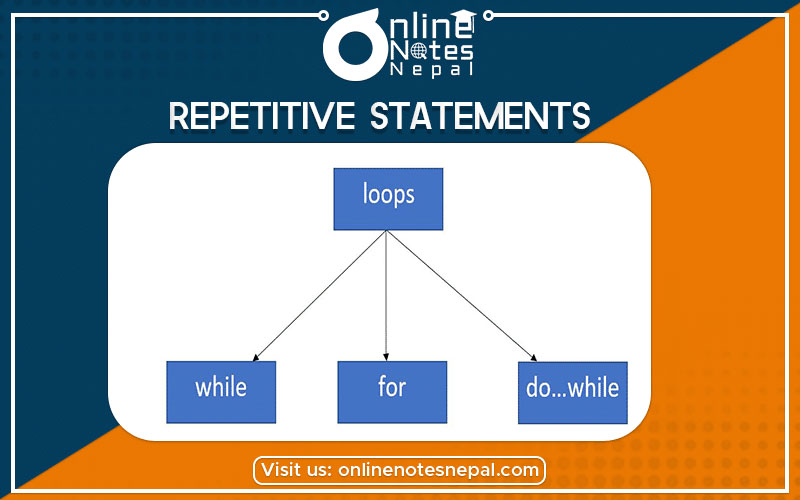
Repetitive statements or looping means executing the same section of code more than once until the given condition is true. A section of code may either be executed a fixed number of times or while the condition is true. C provides three looping statements:
For statement makes programming more convenient to count iterations of a loop and works well, where the number of iterations of the loop is known before the loop entered.
Syntax:
for (initialization; test condition; loop update)
{
Statement(s);
}
Flowchart:
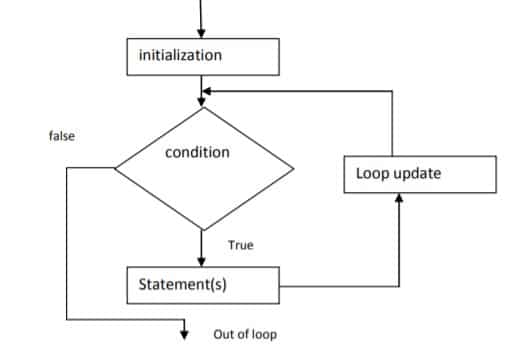
The main purposed is to repeat statements while the condition remains true, like the while loop. But in addition, for provide places to specify an initialization instruction and an increment or decrement of the control variable instruction. So this loop is specially designed to perform a repetitive action with a counter.
For loop has the four parts and it works as:
Examples:

A while loop statement in C programming language repeatedly executes a target statement as long as a given condition is true.
Syntax :
while(condition)
{
statement(s);
}
Flowchart:
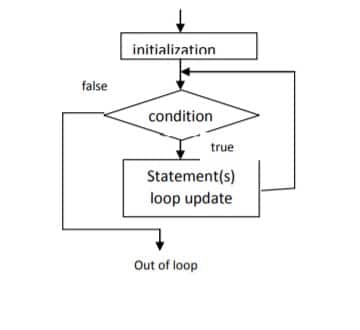
Here, statement(s) may be a single statement or a block of statements. The loop iterates while the condition is true. When the condition becomes false, program control passes to the line immediately following the loop.
Examples:

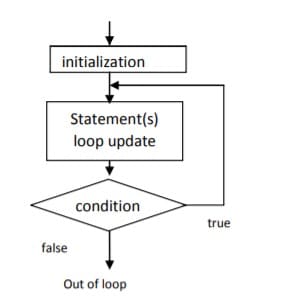
In C, do...while loop is very similar to while loop. The only difference between these two loops is that, in while loops, test expression is checked at first but, in the do-while loop, code is executed at first then the condition is checked. So, the code is executed at least once in do-while loops.
Syntax :
do
{
statement(s);
}while(condition);
Flowchart:
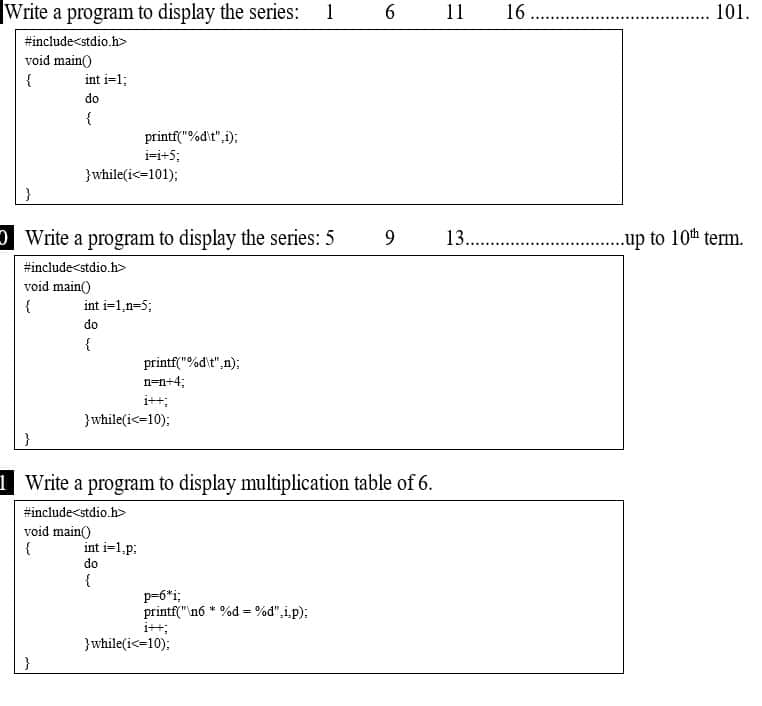
Examples:
| While | do-while |
|---|---|
| It is an entry control loop. | It is an exit control loop. |
| The test condition is evaluated before the loop is executed. | The test condition is evaluated after the loop is executed. |
| It uses a keyword while. | It uses keywords do and while. |
| Loop is not terminated with a semicolon. | Loop is terminated with a semicolon. |
| It doesn’t execute the body of loop until and unless the condition is true. | The body of the loop is always executed at least once since the test condition is not checked until the end of the loop. |
| Example: #include void main() { int i; i=1; while(i<=5) { printf("%d\n",i); } |
Example: #include void main() { int i; i=1; do { printf("%d\n",i); } while(i<=5); |