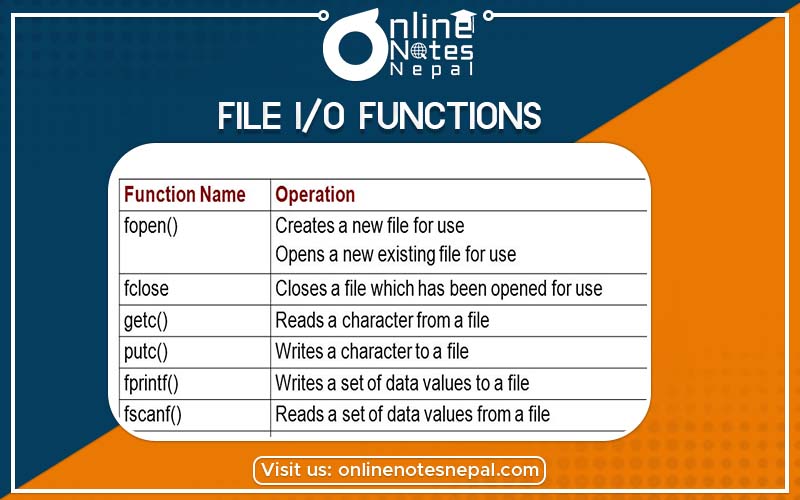
File I/O Functions
Once a file is opened, reading out of or writing to it is accomplished using the standard I/O functions.
String I/O Functions
Using string I/O functions fgets() and fputs(), data can be read from a file or written to a file in the form of an array of characters.
fgets()
- fgets() is used to read a string from the file.
- Syntax: fgets(string,int_value, ptr_var);
Here, int_value denotes the no. of characters in the string.
fputs()
- is used to write a string to file.
- Syntax: fputs(string, ptr_var);
Character I/O Functions
Using character I/O functions fgetc() and fputc(), data can be read from the file or written onto the file one character at a time.
fgetc()
- is used to read a character from a file.
- Syntax: identifier = fgetc (file pointer);
- Example:
FILE *fp;
fp=fopen(“input.txt”,”r”);
char ch;
ch = fgetc (fp);
fputc()
- Write a single character to the output file, pointed to by fp.
- Syntax : fputc('character or character_variable',fp);
- Example:
FILE *fp;
char ch;
fputc (ch,fp); /* writes character ch to a file pointed by file pointer fp*/
Note:
- The routine: getc(fp) is similar to getchar() and
- The routine putc(c,fp) is similar to putchar(c).
Formatted I/O Functions
USing formatted I/O functions, fprintf(), and fscanf(), numbers, characters, or string can be read from a file or written onto a file according to our required format.
fprintf()
- fprintf() is a function used for formatted output in file a file same as printf() does in stardard I/O
- Syntax: fprintf (fp,“format_string",variables);
- Example:
int i = 12;
float x = 2.356;
char ch = 's';
FILE *fp;
fp=fopen(“out.txt”,”w”);
fprintf (fp, "%d %f %c", i, x, ch);
fscanf()
- fscanf() is a function used for formatted input in file a file same as printf() does in stardard I/O
- Syntax: fscanf (fp,“format_string",identifiers);
- Example:
FILE *fp;
Fp=fopen(“input.txt”,”r”);
int i;
fscanf (fp,“%d",i);
Integer I/O Functions
putw()
- is used to write an integer value to the file pointed by file_pointer.
- Syntax: putw(integer,fp);
getw()
- returns the integer value from the file associated with file_pointer.
- Syntax: getw(fp);
/*Example program for using getw and putw functions*/
#include< stdio.h >
main()
{
FILE *f1,*f2,*f3;
int number I;
printf(“Contents of the data file\n\n”);
f1=fopen(“DATA”,”W”);
for(I=1;I< 30;I++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&number);
if(number==-1)
break;
putw(number,f1);
}
fclose(f1);
f1=fopen(“DATA”,”r”);
f2=fopen(“ODD”,”w”);
f3=fopen(“EVEN”,”w”);
while((number=getw(f1))!=EOF) /* Read from data file*/
{
if(number%2==0)
putw(number,f3); /*Write to even file*/
else
putw(number,f2); /*write to odd file*/
}
fclose(f1);
fclose(f2);
fclose(f3);
f2=fopen(“ODD”,”r”);
f3=fopen(“EVEN”,”r”);
printf(“\n\nContents of the odd file\n\n”);
while(number=getw(f2))!=EOF)
printf(“%d%d”,number);
printf(“\n\nContents of the even file”);
while(number=getw(f3))!=EOF)
printf(“%d”,number);
fclose(f2);
fclose(f3);
}
Block I/O Functions
fread ()
- is used to read an entire block from a given file.
- Declaration: size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t n, FILE *stream);
- Remarks:
fread() reads a specified number of equal-sized data items from an input stream into a block.
ptr = Points to a block into which data is read
size = Length of each item read, in bytes
n = Number of items read
stream = file pointer
- Example:
#include
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
char buffer[11];
if(fp=fopen("file1.c","r"))
{
fread(buffer,1,10,fp);
buffer[10]=0;
fclose(fp);
printf("First 10 characters of the file :\n%s\n",buffer);
}
getch();
return 0;
}
fwrite()
- is used for writing an entire block to a given file.
- Declaration: size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t n, FILE*stream);
- Remarks:
fwrite() appends a specified number of equal-sized data items to an output file.
ptr = Pointer to any object; the data written begins at ptr
size = Length of each item of data
n =Number of data items to be appended
stream = file pointer
- Example:
#include
int main()
{
char a[10]={'1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','a'};
FILE *fp;
fp=fopen("Project.txt","w");
fwrite(a,1,10,fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
End of File(EOF)
- There are a number of ways to test for the end-of-file condition.
- Another way is to use the value returned by the fscanf function:
FILE *fptr1;
int istatus ;
istatus = fscanf (fptr1, "%d", &var) ;
if ( istatus == feof(fptr1) )
{
printf ("End-of-file encountered.\n”) ;
}
- EOF is special constant used to check the End of file condition
if( getc(fp)== EOF )
{
printf(“End of file Reached.\n”);