Published by: Zaya
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
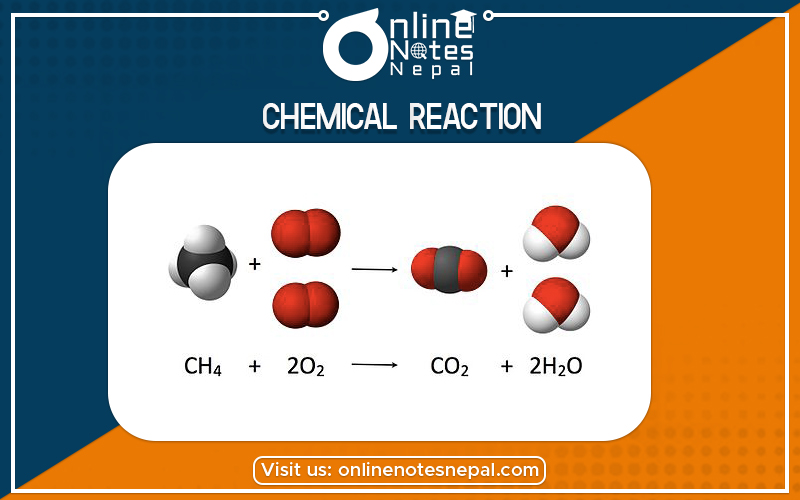
Chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products. Substances are either chemical elements or compounds. A chemical reaction rearranges the constituent atoms of the reactants to create different substances as products.
Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to give calcium chloride water and CO2. This chemical reaction can be written as:
CaC03 + dil 2HCL → CaCl2 + H20 + CO2
40+12+48 2(1+35.5) 40+71 2+16 12+32
=100 =73 =111 =18 =44