Published by: Nuru
Published date: 23 Jan 2022
Respiration
Respiration starts with breathing and process of exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and cells of the human body.
OR
Respiration is the process that begins with inhaling fresh oxygenated air.
It is a vital process in which oxygen is inhaled to oxidize the food for the release of energy and removal of carbon-dioxide gas. The process of respiration continues non-stop from birth to death of a person. The rate of breathing increases, when we are playing, walking, working, reading, writing, thinking and so on. The normal rate of respiration for a healthy adult is about 16 times per minute.
The process of supplying pure oxygen to the cells and eliminating the carbondioxide out of the body is called breathing. Similarly, the process of burning of food in the cells to produce energy in the body is called respiration. There should be continuous supply of oxygen gas to all the cells of our body for their survival. We know that without oxygen, all the vital functions of the cells are stopped which leads to immediate death of cells.
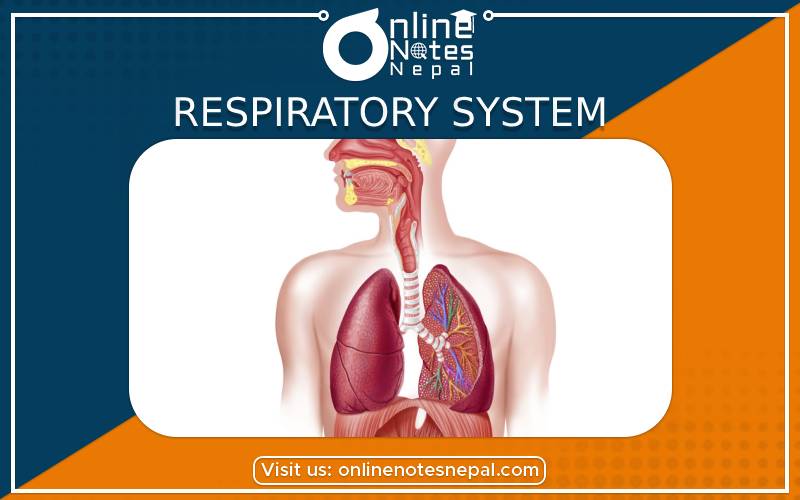
Respiration is also the process in which the oxygen-rich is inhaled and passed through nose, pharynx, larynx, wind pipe, bronchus, bronchiolesn and finally into the lungs and the oxygen gas is exchanged with carbon dioxide gas. The respiratory system, includes air passages, pulmonary vessels, the lungs, and breathing muscles, aids the body in the exchange of gases between the air, blood, and the body’s billions of cells.
The respiratory system filters, warms, and humidifies the air you breathe. Organs in the respiratory system also play a role in speech and the sense of smell. Respiration can be internal as well as external. External Respiration is the one in which the exchange of gases take place within the lungs between blood and external environment. Similarly, Internal Respiration is the one in which exchanges of gases take place between cells and blood.
The respiratory system consists of following organs:
a. Nose
Nose is the only external organ in the respiratory syatem. It consists of two nostrils. It is formed by two nasal bones and cartilage. The air enters through the nose inside which the air is filtered through cilia. The sticky mucous membrane lining the nasal cavity traps dust particles, and tiny hairs called cilia help move them to the nose to be sneezed or blown out. The nose helps to detect the smell of the substances as well.
b. Pharynx
The air from the nose enters to the pharnyx. It starts from the back of the tongue. It is also the common way to both food and air. This organ lies behind the nose, mouth, and larynx. Both food and air pass through the pharynx before reaching their appropriate destinations. The pharynx also plays a role in speech.
c. Larynx
Pharynx leads to the larynx. It extends from the base of tongue to the wind pipe. The Larynx has smaller circular base but upper part is bigger. Larynx is also known as the sound box and responsible for the production of sound. It is essential to human speech. It helps to throw out carbondioxide during exhalation. When the air is forced through the larynx, the vocal cords vibrate and produce the sounds.
d. Wind pipe
The air is passed from larynx to wind pipe. Wind pipe is ahard flexible pipe made of rings of cartilage that joins larynx to bronchi. This tube is about 10-12 cm. It is located just below the larynx, the trachea( wind pipe) is the main airway to the lungs. Trachea divides into right and left bronchi leading to the lungs.
e. Bronchus
The windpipe divides into two branches which are called bronchi. It enters each lung to the right and left. The air inhaled through the nose passes through the pharynx, larynx, wind pipe and finally enters through the bronchus and passes to the numerous bronchioles.
f. Bronchioles
The bronchi divide and redivide to form the finest branches called bronchioles. As the bronchi gets subdivided, they branch into smaller and smaller tubes. The smallest bronchus is called a bronchiole. The bronchioles are made of muscular, fibrous and elastic tissue.
g. Lungs
Lungs are safely protected inside the ribs. The lungs also form one of the body’s largest organs. It is spongy, soft and conical organs. They are covered with two layers of thin members called pleura. They’re responsible for providing oxygen to capillaries and exhaling carbon dioxide. The lungs has network of bronchioles, alveoli, capillaries, arteries and veins.
h. Diaphragm
A thin band of one-shaped muscles which supports the lungs is called diaphragm. It is an inverted U- shaped muscle along the top of abdominal cavity. It separates the chest from stomach and helps the lungs to expand and contract. The expansion and contraction of these muscles help in the respiration process.
i. Intercostal muscles
The eleven pairs of intercostal muscles lies between the spaces of twelve pairs of ribs. Similarly, the expansion and contraction of these muscles plays a great role in respiration. The intercostal muscles are also equally important organs for respiratory system.
j. Pulmonary vein
Pulmonary veins are the parts of circulatory system. Pulmonary vein is one of four vessels that carry aerated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are the only veins that carry bright-red oxygenated blood.
k. Pulmonary artery
The pulmonary artery transports blood from the heart to the lungs. While most major arteries branch off from the aorta. The main pulmonary artery extends from the right ventricles of the heart and branches into left and right pulmonary arteries.
Respiration is the process of inhalation of atmospheric air into lungs due to the contraction of intercostal muscles and oxidizing food to produce energy and throwing out carbondioxide to sustain life. When air enters the lungs, chest expands along with the lungs. The air pressure in the lungs becomes lesser than outer atmospheric pressure and the air enters into lungs. From the lungs carbondioxide gas is expelled out through the same route which completes the respiration.
Respiration is an essential and important process in all living organisms. It helps in the exchange of gases andprovide oxygen which is very important for the survival of most of the life forms on earth. Respiration is something we all know about as it is a visible and regular process, one which we experience with every breath. An adult breathes for about 18-20 times in a minute inrest condition. Similarly, the rate of breathing increases when we involve in games, sports and during anxiety, anger, happiness, etc.
Functions of respiratory system are as follows: